|
#1
30th September 2012, 01:01 PM
|
|||
|
|||
What is the full syllabus of computer science?
what is the full syllabus of computer science?...pelase tell me what is it
|
|
#2
6th October 2012, 11:24 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Quote:
Syllabus for B.Sc(Computer Science) :: -->> Language (Tamil/Telugu/Hindi) -->> English Language -->> Mathematics Paper -->> Digital Logic fundamentals -->> Operating System -->> Programming in C -->> C Lab -->> C++ and Data Structure -->> Data Structure using c++ Lab -->> MicroProcessor & It is applications -->> Software engineering -->> RDMBS with Oracle -->> Programming in C# -->> C# Lab -->> Computer Organization -->> System Programming -->> Data Structure Using Lab -->> Cobol Programming -->> Cobal Lab -->> Object Oriented Analysis and Design -->> Programming in Visual basic -->> Programming in Java -->> VB and Java lab -->> Asp.Net and it is Applications -->> computer Networks -->> Mini Project Eligibility Criteria for B.Sc / B.C.A :: You must have a possessing the intermediate with Physics , Chemistry , mathematics and Computer Science or Biology from a recognized School or equivalent qualification and must secure at least 60% aggregate marks in your examination . 55% marks for reserved categories . Books for Computer Science :: -->> The C Programming Language by Brian W. Kernighan, Dennis M. Ritchie Publisher: PHI Learning Price: Rs. 175 -->> Data Structures Using C Language by Yaduvir Singh, Ashish Agrawal, Amit Agrawal Publisher: Galgotia Publications Pvt. Ltd Price: Rs. 250 -->> The C++ Programming Language by Bjarne Stroustrup Publisher: Pearson Price: Rs. 775 -->> C++ Programming Language by D. S. Malik Publisher: Cengage Learning India Price: Rs. 525 -->> Java: The Complete Reference by Herbert Schildt Publisher: Tata Mcgraw Hill Education Private Limited Price: Rs. 550 -->> Digital Fundamentals by Thomas L. Floyd Publisher: Pearson Price: Rs. 599 -->> Programming with Java by E Balagurusamy Publisher: Tata McGraw-Hill Education Price: Rs. 340 -->> Fundamentals of Digital Circuits by A. Anand Kumar Publisher: PHI Learning Price: Rs. 395 |
|
#3
6th October 2012, 11:42 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Your question is a bit confusing .
Which syllabus do you want ? Entrance or course syllabus ? Which qualification you are talking about ? Computer Science in B.Tech / M. Tech / BCA/ MCA/ B.Sc ...?? Please clarify. |
|
#4
10th October 2012, 11:35 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Quote:
Eligibility Criteria for B.Sc You must have a possessing the intermediate with Physics , Chemistry , mathematics and Computer Science or Biology from a recognized School or equivalent qualification and must secure at least 60% aggregate marks in your examination . 55% marks for reserved categories . Syllabus for B.Sc(Computer Science) :: English Language
Mathematics Paper Digital Logic fundamentals Operating System Programming in C C Lab C++ and Data Structure Data Structure using c++ Lab MicroProcessor & It is applications Software engineering System Programming Data Structure Using Lab Cobol Programming Object Oriented Analysis and Design Programming in Visual basic Programming in Java VB and Java lab Asp.Net and it is Applications computer Networks |
|
#5
11th October 2012, 01:56 AM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Hi friend,
Eligibility Criteria of B.sc.: You must have a possessing the intermediate with Physics , Chemistry , mathematics and Computer Science or Biology from a recognized School or equivalent qualification and must secure at least 60% aggregate marks in your examination . 55% marks for reserved categories . I am attaching the pdf file of the full syllabus of the computer science. ALL THE BEST. |
|
#6
11th October 2012, 08:40 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Computer Science Syllabus :
Basics of Computers Ms-Office C C++ Data Structure Internet DBMS Computer Networking Business System Java Oracle HTML HML SQL Network Security Data Mining & Data Ware housing 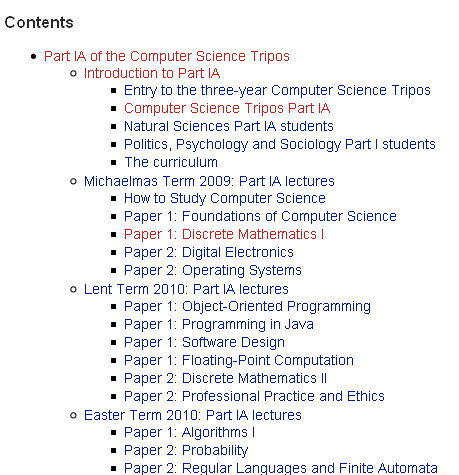
|
|
#7
11th October 2012, 11:04 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Hai
am giving some of information about the syllabus of Computer Science. B.Sc(Computer Science) Syllabus: *English Language * Language (Tamil/Telugu/Hindi) * Digital Logic fundamentals * Operating System * Mathematics Paper * C++ and Data Structure * Programming in C * Data Structure Using Lab * C Lab * Data Structure using c++ Lab * Software engineering * Cobal Lab * C# Lab * MicroProcessor & It is applications * RDMBS with Oracle * Object Oriented Analysis and Design * Programming in Visual basic * Programming in C# * Asp.Net and it is Applications * computer Networks * Computer Organization * System Programming * Cobol Programming * Programming in Java * VB and Java lab * Mini Project ALL THE BEST........ |
|
#8
12th October 2012, 06:37 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Hi Friend........
Syllabus for Computer Science........... English Second Language Operation Systems Mathematics Digital Logics C++ Data Structure C programming Cobal Micro Processor & Applications RDBMS System Programming Computer Organizations Cobol Programming Asp.Net & Applications VB and Java Mini Project. |
|
#9
13th October 2012, 08:26 AM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Hai,
Syllabus of computer science:-  C++, C, Oracle, Java, DBMS, RDBMS With oracle, MS-Office, HTML, DHTML, Cobol programming, Computer organisation, Computer networking, Data ware housing and data mining, System programming, VB and java lab, .Net, Internet, Data structures using lab. |
|
#10
2nd November 2012, 06:25 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
your question is quite well confusing....... but making as a random choice that you might be a B. tech student ...... the syllabus is as :
SYLLABUS FOR B.TECH(Bachelor of Technology) STUDENTS : Since its an 8-semesters course , the whole structure(from 3rd sem. to 8th sem.) is as : SEMESTER-III NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND PROGRAMMING (MA 3103) Numerical computation and error, solution of algebraic and transcendental equations- Bisection method, Regula-Falsi method and Newton-Raphson method and their order of convergence. Iterative methods for system of non-linear equations. Linear system of equations: Gauss elimination method, Crout’s method, Jacobi’s method, Gauss-Seidel method. Computer programming of above methods. 16 L Finite differences, difference operators and symbolic relations, difference of a polynomial, Interpolation ,error in interpolation, Newton’s forward and backward formulae, Lagrange’s interpolation formula, Newton general interpolation formula, Numerical differentiation, error in numerical differentiation. Numerical integration: Newton’s cote’s formula, Trapezoidal rule, Simpson 1/3 rule, Simpson 3/8 rule and their error estimation. Computer programming of above methods. 16 L Ordinary differential equations: Taylor’s series method, Euler’s method, Euler’s modified method, Runge-Kutta method, Boundary value problem-linear and non-linear equations. Computer programming of above methods. 10 L MATERIAL SCIENCE (B) (PH 3103) Introduction: - Material Science and Engineering, classification of engineering materials, structure property relationship in materials, introduction to metals & alloys, Ceramics, polymers, composites. 03L Crystal Geometry: Introduction, the space lattices, and lattice points, Unit cell and primitive cell, crystal systems, Bravias lattices, crystal direction and planes, reciprocal lattice, Miller indices, coordination number and atomic packing factor and its determination for simple cubic and Hexagonal closed packed structure. Determination of crystal structure by X – ray diffraction. 07L Crystal Imperfections: Introduction, Classification of imperfection, Point, line and surface imperfection. 03L Phase Diagrams: The phase rule, single component system, Binary phase diagrams, and the lover rule. The iron-iron carbide phase diagram, Hume – Rothrey rules of alloying. Oxidation and Corrosion: Oxidation, mechanism of oxidation, oxidation resistant materials, Corrosion, The principle of corrosion, various forms of corrosion, Protection against corrosion. 04L Diffusion in solids: Introduction, types and mechanism of diffusion, Fick’s law of diffusion, the atomic model of diffusion. Experimental determination of diffusion coefficient, The Kirkendall effect. 05L Dielectrics: Introduction, Dielectric polarization, types of polarization, Temperature and frequency effects, Ferro electricity, and piezoelectricity. 04L Magnetic properties: Diamagnetism, paramagnetism, ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism, soft and hard magnetic materials, magnetic moment due to electron spin 05L Electrical properties : The free electron theory, Fermi- Dirac distribution function, conduction by free electron, Mobility and conductivity, energy band theory of solids, Insulators, semiconductors, metals, potential field in a metal, bond and free electron, Superconductivity and superconducting materials, Type I and Type II superconductors, The Meissner’s effect. MATHEMATICS – III (MA 3104) LAPLACE TRANSFORMATION :- Definition of Laplace transform and linearity and shifting property, Laplace transform of elementary functions, Inverse Laplace transform, Laplace transform of derivative and integration, convolution theorem, Solution of differential equation by Laplace transform, Unit Step function, Unit impulse function. 09 L VECTOR CALCULUS :- Differentiation of vector function, gradient, divergence, curl and their geometrical or physical interpretation, Line, Surface and Volume integrals, Statement of Green’s Theorem , divergence theorem and Stoke’s theorem and their applications. Curvilinear co-ordinates. 09 L FOURIER SERIES :- Fourier series, Dirichlet’s conditions, Half Range series. 04 L FOURIER TRANSFORM :- Definition of Fourier Transform, linearity, shifting, frequency theorem, Fourier transform of derivatives and Dirac-delta function, Inverse Fourier transform, Fourier Sine and Cosine transform, Solution of simple differential equation by Fourier transform method. 10 L Z- TRANSFORMATION :- Definition, Z-transformation of standard sequences, linearity property, Shifting theorem, inverse of Z-transformations, Scaling property of Ztransformation, differentiation of Z-transformation, convolution of sequences, solution of difference equations by Z-transformation. DATA STRUCTURE (CS 3101) Overview of C language [ 6 L ] Time and Space analysis of Algorithms - Order Notations. Linear Data Structures - Sequential representations - Arrays and Lists, Stacks, Queues and Dequeues, strings, Application. [ 6 L ] Linear Data Structures, Link Representation - Linear linked lists, Circularly linked lists. Doubly linked lists, application. [ 6 L ] Recursion - Design of recursive algorithms, Tail Recursion, When not to use recursion, Removal of recursion. [ 4 L ] Non-linear Data Structure: Trees - Binary Trees, Traversals and Threads, Binary Search Trees, Insertion and Deletion algorithms, Height-balanced and weight-balanced trees, Btrees, B+ -trees, Application of trees; Graphs - Representations, Breadth-first and Depth-first Search. [10 L ] Hashing - Hashing Functions, collision Resolution Techniques. [ 4L] Sorting and Searching Algorithms- Bubble sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort, Quick Sort, Merge Sort, Heap sort and Radix Sort. [ 6 L ] File Structures - Sequential and Direct Access. Relative Files, Indexed Files - B+ tree as index. Multi-indexed Files, Inverted Files, Hashed Files. DIGITAL ELECTRONICS & INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (EC 3102) Number systems, Binary representation, Codes and their conversions: BCD, Octal, Hexadecimal, ASCII, EBDIC, Gray, Signed binary number representation with 1’s and 2’s complement methods, Binary arithmetic. 5L Boolean algebra, Venn diagram, logic gates and circuits, Minimization of logic expressions by algebraic method, K-map method and Quine Mc Clauskey method 8L Combinational circuits- adder, subtractor, encoder, decoder, comparator, multiplexer, de-multiplexer, parity generator. 6L Design of combinational circuits-Programming logic devices and gate arrays. 2L Sequential Circuits- Flip Flops, various types of Registers and counters and their design, Irregular counter, State table and state transition diagram, sequential circuits design methodology 8L Different types of A/D and D/A conversion techniques. 5L Different Logic families- TTL, ECL, MOS and CMOS, their operation and specifications. 4L Memory Systems: RAM, ROM, EPROM,EEROM 2L PRINCIPLE OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES (IT 3102) Concepts of structural program development; concept of data types; precedence and associativity of operators; conditional transfer; deterministic and in-deterministic loops; Recursions; functions and procedures - call by value, call by reference and their differences; programming for numerical methods; records. Data-type handling and various constructs (conditional, loop, functions etc); pointers: concept of pointers and passing parameters using pointers, non-numeric processing, concept of arrays of pointers and pointers to pointers; [8 L ] structures and unions – advantage of using structures, concept of information hiding, pointers to structures; files - basic concept of various types of file access methods: sequential, indexed sequential, random, various statements for file handling [ 8 L ] Advanced Programming Languages like C++, ADA, LISP, PROLOG, and PASCAL. Comparison of various languages SEMESTER-IV MATHEMATICS – IV (MA 4105) SPECIAL FUNCTIONS :- Series solution of differential equations, Bessel and Legendre’s equations and their series solution, elementary properties of Bessel’s function and Legendre’s polynomial. 12 L COMPLEX VARIABLE:- Analytic function, Cauchy- Riemann equation. Complex Integration, Cauchy’s theorem and Cauchy Integral formula. Taylor and Laurent’s expansion. Poles and Residue, Residue theorem. Conformal transformation, Bilinear and Schwartz’s transformations. . 15 L PARATIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION :- Formulation of partial differential equation, Linear and non-linear partial differential equations of the first order, Lagrange’s method and Charpit’s method. Higher order Partial Linear differential equations with constant coefficients. Method of separation of variables. Equation of vibrating strings, heat flow, Laplace’s two dimensional equation and simple problems. PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS (MA 4106) Probability: classical and axiomatic definitions, addition law, conditional probability, multiplication law, total probability, Baye’s theorem and independence of events. Random variables: Discrete and continuous random variables, probability mass, probability density and commutative distribution functions. Mathematical expectation, variance, moment and moment generating function, Chebyshev ‘s inequality.10 L Regression Analysis: Linear regression, principle of least square, non-linear regression, correlation, coefficient of correlation, Rank correlation. 05 L Distributions: Binomial, Hypergeometric, Geometric, Poisson and Normal distributions. Sampling Distribution: Population samples, sampling distribution, estimate for population mean and variance, point of estimation, confidence interval for mean and variance of normal population, Testing of hypothesis, the critical and acceptance region, two type of errors, Chi-square, t-student and F distributions. 12 L Analysis of Variance: completely randomize design and randomized block design, Quality control, control charts(X-chart, R-chart, P-chart and C-chart). ANALOG ELECTRONICS (EC 4103) Transistor Biasing and Stability: Self Bias-CE, CC, Compensation techniques. Voltage, current, transresistance & transconductance amplifier. 6L High frequency model of transistor. 2L Power amplifiers – Class A, B, AB, C, Tuned amplifier.Push –pull amplifiers. 6L Operational Amplifier: Differential Amplifier using BJT and FET,Internal structuer of Op-amp, C onstant current source (current mirror etc.), level shifter, Ideal and practical OpAmp. Comparator, Schmitt Trigger. Instrumentation Amplifier, Log & Anti-log amplifiers, Trans-conductance multiplier,Linear &Nonlinear Precision Rectifier 10L Multivibrator – Monostable, Bistable, Astable.Ckts & Timer. Monostable and astable operation using 555 timer. 6L Linear voltage regulator : series and shunt. Switched mode power supply. 4L Function generator, wave shapers. V-I, I-V, V-F & F-V converters. VCO, PLL lock-in amplifier. 6L COMMUNICATION SYSTEM & ENGG. (EC 4104) 1. 1. Wave spectra: Introduction, spectral analysis of respective waves. 2. Noise: Introduction, Thermal noise, S/N ratio, Equivalent Noise Resistance, Noise Factor, Noise Temperature. 3. Modulation and demodulation of signals: (i) Amplitude Modulation, Frequency spectrum, Average power, Diode envelope detection. (ii) SSB modulation, Principles, FET Balanced Modulators, SSB Generation by Phase shift method. (iii) FM and PM: Frequency spectra, Equivalence between FM and PM, FET Reactance Modulator, The Armstrong method, FM stereo Broad Transmitter, Foster seely Discriminator, Pre-emphasis and De-emphasis. Automatic Frequency control. 4. Performance of Communication Systems. Noise in Amplitude Modulated systems and Angle modulated systems. 5. Super heterodyne Receivers (Block diagram treatment) choice of IF and Oscillator frequency, Image rejection. 6. Sampling Theorem, Pulse Modulation, Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Time Modulation, TDM, FDM. 7. Digital Communication: Pulse code modulation, Delta Modulation, Quantization Noise in Binary PCM, Digital carrier systems: ASK, FSK, PSK, and DPSK. 8. Introduction to Information theory, Measure of information channel capacity, exchange of BW for S/N ratio. MICROPROCESSOR AND INTERFACING (EE 4107) Introduction to 8085A CPU architecture-register organization, addressing modes and their features. Software instruction set and Assembly Language Programming. Pin description and features. Instruction cycle, machine cycle, Timing diagram. Hardware Interfacing: Interfacing memory, peripheral chips (IO mapped IO & Memory mapped IO). Interrupts and DMA. Peripherals: 8279, 8255, 8251, 8253, 8237, 8259, A/D and D/A converters and interfacing of the same. Typical applications of a microprocessor. 16 bit processors: 8086 and architecture, segmented memory has cycles, read/write cycle in min/max mode. Reset operation, wait state, Halt state, Hold state, Lock operation, interrupt processing. Addressing modes and their features. Software instruction set (including specific instructions like string instructions, repeat, segment override, lock prefizers and their use) and Assembly Language programming with the same. Brief overview of some other microprocessors (eg. 6800 Microprocessor). SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (CS 4102) Software Quality [12L] Software Quality Assurance, Software Metrics, Software Validation, Static and Dynamic Analysis, Symbolic Equation, Mutation Analysis, Dynamic Testing, Unit Testing, White-box and Black-box Testing, Test Case Generation, Integration Testing, Bottom-up and Top-down Testing, System Testing, Function Testing, Performance Testing, Acceptance Testing, Installation Testing, Theoretical Foundation of Testing, Formal Verification, Test tools. User Interface [10L] Module Introduction, Objectives of Usability, How to Approach Usability, Designing with Usability in mind, Measuring Usability, Guidelines for User Interface Design, User Interface Elements, Dialog Design, SSADM, Methodology for Dialog Design, Prototyping Tools. Software Reliability [10L] Reliability, Hazard, MTTF, Repair and Availability, Steady-State Availability, Estimation of Residual Errors, Reliability Models, Software Complexity, Cyclomatic Complexity, Halstead’s Metrics. Project Management [12L] Issues in Project Management, Management Functions, Software Project Management Plan, Software Management Structure, Personnel Productivity, Software Project Complexity, Software Metrics – Basic Consideration, Size Oriented and Function Point Oriented; Software Cost Estimation Techniques, Algorithmic Cost Modeling, The COCOMO Model, Project Scheduling, Software Project Planning, Scheduling Risk Management. SEMESTER-V OPERATING SYSTEMS (CS 5103) Introduction [4L] Introduction to OS. Operating system functions, evaluation of O.S., Different types of O.S.: batch, multi-programmed, time-sharing, real-time, distributed, parallel. System Structure[3L] Computer system operation, I/O structure, storage structure, storage hierarchy, different types of protections, operating system structure (simple, layered, virtual machine), O/S services, system calls. Process Management [17L] Processes [3L]: Concept of processes, process scheduling, operations on processes, cooperating processes, inter-process communication. Threads [2L]: overview, benefits of threads, user and kernel threads. CPU scheduling [3L]: scheduling criteria, preemptive & non-preemptive scheduling, scheduling algorithms (FCFS, SJF, RR, priority), algorithm evaluation, multi-processor scheduling. Process Synchronization [5L]: background, critical section problem, critical region, synchronization hardware, classical problems of synchronization, semaphores. Deadlocks [4L]: system model, deadlock characterization, methods for handling deadlocks, deadlock prevention, deadlock avoidance, deadlock detection, recovery from deadlock. Storage Management [19L] Memory Management [5L]: background, logical vs. physical address space, swapping, contiguous memory allocation, paging, segmentation, segmentation with paging. Virtual Memory [3L]: background, demand paging, performance, page replacement, page replacement algorithms (FCFS, LRU), allocation of frames, thrashing. File Systems [4L]: file concept, access methods, directory structure, file system structure, allocation methods (contiguous, linked, indexed), free-space management (bit vector, linked list, grouping), directory implementation (linear list, hash table), efficiency & performance. I/O Management [4L]: I/O hardware, polling, interrupts, DMA, application I/O interface (block and character devices, network devices, clocks and timers, blocking and nonblocking I/O), kernel I/O subsystem (scheduling, buffering, caching, spooling and device reservation, error handling), performance. Disk Management [3L]: disk structure, disk scheduling (FCFS, SSTF, SCAN,C-SCAN) , disk reliability, disk formatting, boot block, bad blocks. Protection & Security [4L] Goals of protection, domain of protection, security problem, authentication, one time password, program threats, system threats, threat monitoring, encryption. DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (CS 5104) Introduction [3L] File & Data Base Concept, Overview of DBMS, Data Models, Database Administrator, Database Users, Schema. Data Independence Entity-Relationship Model [3L] Basic concepts , Keys, Entity-Relationship Diagram, Cardinality ratios, Strong & Weak Entity Sets, Specialization, Generalization, Aggregation. Relational Model [4L] Procedural & Non Procedural Languages, Relational Algebra, Extended Relational Algebra Operations, Views, Modifications Of the Database, Relational Calculus . SQL [5L] Basic Concepts, Set operations, Aggregate Functions, Null Values, assertions, views, Nested Sub-queries, Cursors, Stored procedures and triggers. Integrity Constraints & Introduction to RDBMS [3L] Domain Constraints, Referential Integrity Constraints, Codd’s rule. Functional Dependencies and Normalization [7L] Functional Dependency, Armstrong’s axioms, Canonical Cover, Closure , Full and Partial Functional dependencies, Prime & Non Prime attribute , 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, Multi valued Dependency , 4NF, 5NF, DKNF . Transaction & Concurrency Control [5L] Transaction concept, ACID properties, Conflict & View serializabilty, Test for Conflict serializability, Concurrency Control, Lock base protocols, Two phase locking. Storage Strategies [4L] Single-Level Index (primary, secondary, clustering), Multi-level Indexes, Dynamic Multilevel Indexes, Hashing Techniques, B tree and B+ tree . Query Optimization [4L] Full Table scan, Indexed-based scan, Merge join, Nested loop join , Equivalence rules , Heuristic Optimization , Cost Based Optimization. Backup & Recovery [3L] Physical & Logical Backup , Transaction logs, Causes of failures , Recovery techniques. Distributed Databases [4L] Basic Concepts, Data Fragmentation, Replication and Allocation Techniques, Types of Distributed Database Systems, Query Processing, Overview of Client-Server Architecture and Its relationship to Distributed Databases. DESIGN & ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS (CS 5105) Models of computation [4L]: Random Access Machine, Relationship between Turing Machine and RAM, Time and Space Complexity. Complexity analysis [8L]: Asymptotic notations, Recurrence for divide and conquer and its solution, Merge sort, Heap sort, Quick sort and their complexity. Dynamic Programming [4L]: Basic method, Matrix-chain multiplication, All pair shortest paths, Single-source shortest path, Travelling Salesman problem. Greedy Method [5L]: Basic method, Knapsack problem, Job sequencing with deadlines, Minimum spanning tree by Prim's and Kruskal's algorithms. Disjoint Set Manipulation [4L]: Set manipulation algorithm like UNION-FIND, Union by rank, Path compression. Graph Traversal Algorithms [5L]: BFS and DFS, Backtracking and its use in solving Knapsack and Eight queens problem. Matrix Manipulation Algorithms [6L]: Strassen’s Matrix-multiplication algorithm and its applications in Solution of simultaneous linear equations using LUP decomposition, Inversion of Matrix and Boolean Matrix multiplication. Notion of NP-completeness [5L]: P class, NP-hard class, NP-complete class, Circuit Satisfiability problem. Approximation Algorithms [4L]: Vertex cover problem, Travelling salesman problem, Set covering problem. COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE (CS 5106) Concepts & Terminology: Digital computer concepts; Von-Neumann concept ; Hardware & Software and their nature ; structure & functions of a computer system , Role of operating system. [ 8 L ] Memory Unit : Memory classification , characteristics ; Organization of RAM , address decoding ROM/PROM/EEPROM ; Magnetic memories , recording formats & methods , Disk & tape units; Concept of memory map , memory hierarchy , Associative memory organization ; Cache introduction , techniques to reduce cache misses , concept of virtual memory & paging. [ 8 L ] CPU Design: The ALU – ALU organization , Integer representation , 1s and 2s complement arithmetic ; Serial & Parallel Address; implementation of high speed Address Carry Look Ahead & carry Save Address; Multiplication of signed binary numbers-Booth’s algorithm ; Divide algorithms- Restoring & Non-Restoring ; Floating point number arithmetic; Overflow detection , status flags. [ 8 L ] Instruction Set Architecture- Choice of instruction set ; Instruction word formats ; Addressing modes. [ 5 L ] Control Design – Timing diagrams; T-States , Controlling arithmetic & logic instruction , control structures ; Hardwired & Micro programmed, CISC & RISC characteristics. [ 6 L ] Pipelining - General concept , speed up , instruction & arithmetic pipeline; Examples of some pipeline in modern processors , pipeline hazards; Flynn’s classification –SISD ,SIMD , MISD , MIMD architectures-Vector and Array processors & their comparison , Concept of Multiprocessor; Centralized & distributed architectures. [ Input/output Organization : Introduction to Bus architecture , effect of bus widths , Programmed & Interrupt I/O , DMA. FORMAL LANGUAGES & AUTOMATA THEORY(CS 5107) Finite State Machines [4L] Definition, concept of sequential circuits, state table & state assignments, concept of synchronous, asynchronous and liner sequential machines Finite State Models [10L] Basic definition, mathematical representation, Moore versus Mealy m/c, capability & limitations of FSM, state equivalence & minimization, machine equivalence, incompletely specified machines, merger graph & compatibility graph, merger table, Finite memory, definite, information lossless & inverse machines : testing table & testing graph. Structure of Sequential Machines [3L] Concept of partitions, closed partitions, lattice of closed partitions, decomposition : serial & parallel. Finite Automation [9L] Preliminaries (strings, alphabets & languages, graphs & trees, set & relations), definition, recognition of a language by an automata - idea of grammar, DFA, NFA, equivalence of DFA and NFA, NFA with e-moves, regular sets & regular expressions : equivalence with finite automata, NFA from regular expressions, regular expressions from DFA, two way finite automata equivalence with one way, equivalence of Moore & Mealy machines, applications of finite automata. Closure Properties of Regular Sets [4L] Pumping lemma & its application, closure properties minimization of finite automata : minimization by distinguishable pair, myhill-nerode theorem. Context Free Grammars [4L] Introduction, definition, derivation trees, simplification, CNF & GNF. Pushdown Automata [5L] Definition, moves, instantaneous descriptions, language recognised by PDA, deterministic PDA, acceptance by final state & empty stack, equivalence of PDA and CFL. Closure Properties of CFLs [4L] Pumping lemma & its applications, ogden’s lemma, closure properties, decision algorithms. Introduction to ZRL & CSL [2L] Introduction to Z. Regular language properties and their grammars, Context sensitive languages. SEMESTER-VI INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT (ME 6123) Human Resource Management: [8L] Recruitment and selection, Performance appraisal, Industrial Relations, Trade Union, Collective Bargaining Organizational Behaviour: [8L] Different Schools of Management Thought : Scientific Management, Administrative Theory, Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relations Theory(Elton Mayo). Motivation: Concept, Different Theories (Maslow, ERG, Herzberg, ) Communication: Purpose, process, Barriers to effective communication, Guidelines to make communication effective. Perception: Process, Importance, Factors influencing perception, Shortcuts for judging people- Halo effect, Stereotyping, Projection. Quality Management: [6L ] Concept, Dimensions for goods and services, Cost of Quality, Statistical Quality Control, Control Charts, Acceptance Sampling (single). Total Quality Management: Concept, benefits, Criticism. New Quality Tools: Kaizen, Six Sigma, Quality Circles. Productions Management: [ 5L ] Concept. Difference from Operations Management, Types of Production( Mass, Batch, Project), Functions of Production Management. Productivity: Concept, Different Inputs and Productivity Measures, Effeciency and Effectiveness, Measures to increase Productivity. Marketing Management: [6L ] Basic Concepts of Marketing, Difference between Selling and Marketing, Elements of Marketing Mix- the 4 P’s. Marketing Environment: Mega Environment, Micro Environment, Internal Environment, Relevant Environment. Simple Marketing Strategies: SWOT Analysis, BCG Matrix, Industry Matrix. Materials Management: [6L ] Concept, Functions, EOQ Models- Wilson model, model with shortage, model with quantity discount, model without shortage , Selective Inventory Control—ABC, VED, FSN analysis. COMPILER DESIGN (CS 6108) Classification of grammars. Context free grammars. [ 6 L ] Deterministic finite state automata (DFA) Non-DFA Scanners. Top down parsing, LL grammars. Bottom up parsing. Polishing expressions Operator precedence grammar. LR grammars. Comparison of parsing methods. Error handling. [ 20 L ] Symbol table handling techniques. Organisation for non-block and block structured languages. Run time storage administration. [ 6 L ] Static and dynamic allocation. Intermediate forms of source program. Polish N-tuple and syntax trees. [ 4 L ] Semantic analysis and code generation. Code optimisation, folding, and redundant subexpression evaluation. Optimisation within iterative loops. SOFT COMPUTING (CS 6109) Introduction to artificial neural network [ 10L ] Neural Networks: History, overview of biological Neuro-system, Mathematical Models of Neurons, ANN architecture, Learning rules, Learning Paradigms-Supervised, Unsupervised and reinforcement Learning, ANN training Algorithms-perceptions, Training rules, Delta, Back Propagation Algorithm, Multilayer Perceptron Model, Applications of Artificial Neural Networks. Competitive learning networks, Kohonen self organizing networks, Hebbian learning; Hopfield Networks, Associative Memories, The boltzman machine; Applications. Fuzzy Logic [ 12L ] Fuzzy Logic: Introduction to Fuzzy Logic, Classical and Fuzzy Sets: Overview of Classical Sets, Membership Function, Fuzzy rule generation. Operations on Fuzzy Sets: Compliment, Intersections, Unions, Combinations of Operations, Aggregation Operations. Fuzzy Arithmetic: Fuzzy Numbers, Linguistic Variables, Arithmetic Operations on Intervals & Numbers, Lattice of Fuzzy Numbers, Fuzzy Equations.Fuzzy Logic: Classical Logic. Genetic algorithms(Gas),Evolution strategies(Ess),Evolutionary programming(EP),Genetic Programming(GP),Selecting,crossover,mutation,schem a analysis,analysis of selection algorithms;convergence;Markov & other stochastic models. [ 10L ] Other Soft computing approaches [ 7L ] Simulated Annealing, Tabu Search, Ant colony based optimisation, etc. COMPUTER NETWORKS (IT 6103) Overview of Data Communications and Networking [2L] Introduction, Network Models Physical Layer [8L] Signals, Digital Transmission, Analog Transmission, Multiplexing, Transmission Media, Circuit Switching and Telephone Network. Data Link Layer [9L] Error Detection and Correction, Data Link Control and Protocol, Point to Point Access :PPP, Multiple Access, Local Area Networks : Ethernet, Wireless Lans, Connecting Lans, Backbone Networks, Virtual Lans, Cellular Telephone and Satellite Networks, Virtual Circuit Switching. Network Layer [8L] Host-to-Host Delivery :Internetworking, Addressing and Routing, Network Layer Protocols : ARP, IPv4, ICMP, IPv6, and ICMPv6, Unicast and Multicast Routing : Routing Protocols. Transport Layer [5L] Process-to-Process Delivery : UDP and TCP, Congestion Control and Quality of Service. Application Layer [9L] Client-Server Model : Socket Interface, Domain Name System (DNS), Electronic Mail (SMTP), and File Transfer (FTP), HTTP and WWW, Multimedia. Security [4L] Cryptography, Message Security, User Authentication, and Key Management, Security Protocols in the Internet. COMPUTER GRAPHICS (CS 6110) Introduction to Computer Graphics & Graphics Systems [4L] Overview of CG, definitions of CG, types of CG, storage tubes displays, CRT technologies - Raster Scan Display, Computer graphics software. Scan Conversion [6L] Points & lines, Line drawing algorithms; DDA algorithm, Bresenham’s line algorithm, Circle generation algorithm; Ellipse generating algorithm; scan line polygon, fill algorithm, boundary fill algorithm, flood fill algorithm. 2D Transformation [8L] Basic transformations: translation, rotation, scaling; Matrix representations & homogeneous coordinates, transformations between coordinate systems; reflection shear; Transformation of points, lines, parallel lines, intersecting lines. Viewing [4L] Viewing pipeline, Window to Viewport co-ordinate transformation, clipping operations, point clipping, line clipping, clipping circles, polygons & ellipse. 3D Transformation & Viewing [10L] 3D transformations: translation, rotation, scaling & other transformations. Rotation about an arbitrary axis in space; reflection through an arbitrary plane; general parallel projection transformation; clipping, Viewport clipping, 3D viewing, perspectives & Depth Cueing. Curves and Fractals [4L] Curve representation, surfaces, designs, Bezier curves, B-spline curves, end conditions for periodic B-spline curves, rational B-spline curves. Hidden Surfaces [4L] Depth comparison, Z-buffer algorithm, Back face detection, BSP tree method, the Printer’s algorithm, scan-line algorithm; Hidden line elimination, wire frame methods, fractal - geometry. Color & Shading Models [5L] Introduction, Modeling Light Intensities and Sources, Diffuse Reflection, Lambert’s Cosine Law, Specular Reflection, Halftoning, Color Models - RGB Color, CMY Color. SEMESTER - VII VLSI DESIGN (EC 7111) Analog VLSI Circuit Design: - i) Review of MOSFET characteristics, scaling and small-geometry effects, MOSFET capacitances. 3 L ii) MOS resistor, MOS current source, current mirror circuits. MOS voltage source Linear voltage and current converters. 3 L iii) CMOS operational amplifier (OPAMP) design: - Differential amplifier, level shifter, source follower, output stage voltage and power amplifiers. Cascode OPAMP. Compensation techniques. 5 L iv) Analog Filters: - Switched capacitor (SC) fundamentals, first order SC circuits, second-order SC circuits and cascade design. 3 L v) Analog to digital and digital to analog converters, speed of conversion and over sampling issues. 4 L vi) VLSI Interconnects: - distributed RC model, transmission line model. Future inter connect technologies. 2 L Digital VLSI Circuit Design: - i) MOS inverters, CMOS inverter, state characteristics, switching characteristics, power dissipation issues. 3 L ii) CMOS logic gates: NAND, NOR, XOR, CMOS logic design of half and full adders. CMOS transmission gates, pseudo-nMOS, domino logic gates. 5 L iii) Sequential MOS Logic Circuits: The SR latch circuit, clocked latch and flip-flop, CMOS D-latch and edge-triggered circuits, Schmitt trigger circuit, Comparator. 4 L iv) Dynamic Logic Circuits: Pass transistor logic, synchronous dynamic circuit techniques. 3 L v) Semiconductor Memories: ROM circuits, SRAM circuits, DRAM circuits, drivers and buffers, Buffer scaling and design issues. 5 L ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & EXPERT SYSTEM (CS 7111) Introduction [2L] :Overview of AI, Problems of AI, AI techniques; Problem Solving - Problem space and search, Defining the problem as state space search, Problem characteristics; Tic-Tac-Toe problem. AI languages [4L] Basic knowledge of programming languages like Prolog and Lisp. Basic Search Techniques [4L] :Solving problems by searching; Uniform search strategies: breadth first search, depth first search, depth limited search, bidirectional search, comparing search strategies in terms of complexity. Special Search Techniques [6L] : Heuristic Search- greedy best-first search, A* search; Hill climbing search, Simulated annealing search; Genetic algorithms; Constraint satisfaction problems; Adversarial search - Games, Optimal decisions and strategies in games, Minimax search, Alpha-beta pruning. Symbolic Logic [5L] :Syntax and semantics for propositional logic, Syntax and semantics of FOPL, Properties of WFF, Clausal form, Unification, Resolution. Reasoning Under Inconsistencies and Uncertainties [3L] :Non-monotonic reasoning, Truth maintenance systems, Default reasoning & closed world assumption, Predicate completion and circumscription, Fuzzy logic. Probabilistic Reasoning [3L] :Bayesian probabilistic inference, Representation of knowledge in uncertain domain, Semantics of Bayesian networks, Dempster-Shafer theory. Structured Knowledge [4L] ::Associative networks, Conceptual graphs, Frame structures. Expert Systems [4L] :Rule based systems, Nonproduction systems: decision tree architectures, blackboard system architectures, neural network architectures. Learning [4L] :Types of learning, general learning model, Learning by induction: generalization, specialization; example of inductive learner. WEB TECHNOLOGY (CS 7112) Static Web Pages [6L] Web Pages - types and issues, tiers; comparisons of Microsoft and java technologies, WWW-Basic concepts, web client and web server, http protocol (frame format), universal resource locator (url), HTML- different tags, sections, image & pictures, listings, tables, frame, frameset, form. Dynamic Web Pages [2L] The need of dynamic web pages; an overview of DHTML, cascading style sheet (css), comparative studies of different technologies of dynamic page creation. Active Web Pages [2L] Need of active web pages; java applet life cycle. Java Script [3L] Data types, variables, operators, conditional statements, array object, date object, string object. Java Servlet [4L] Servlet environment and role, HTML support, Servlet API, The servlet life cycle, Cookies and Sessions. JSP [15L] JSP architecture, JSP servers, JSP tags, understanding the layout in JSP, Declaring variables, methods in JSP, inserting java expression in JSP, processing request from user and generating dynamic response for the user, inserting applets and java beans into JSP, using include and forward action, comparing JSP and CGI program, comparing JSP and ASP program; Creating ODBC data source name, introduction to JDBC, prepared statement and callable statement. J2EE[7L] An overview of J2EE web services, basics of Enterprise Java Beans, EJB vs. Java Beans, basics of RMI, JNI. XML [6L] Extensible Markup Language (XML), basics of XML, elements and attributes, document type definition, XML parsers, sequential and tree approach. ELECTIVES I & II PARALLEL PROGRAMMING (CS 7114) Processes and processors. Shared memory. Fork. Join constructs. Basic parallel programming techniques- loop splitting, spin locks, contention barriers and row conditions. [ 12 L ] Variations in splitting, self and indirect scheduling. Data dependency-forward and backward block scheduling. Linear recurrence relations. Backward dependency. Performance tuning overhead with number of processes, effective use of cache. [ 12L ] Parallel programming examples: Average, mean squared deviation, curve fitting, numerical integration, travelling salesman problem, Gaussian elimination. Discrete event time simulation. [ 10 L ] Parallel Programming constructs in HPF, FORTRAN 95. Parallel programming under Unix. DATA WAREHOUSING AND DATA MINING (CS 7115) Introduction [2L] : Data warehousing – definitions and characteristics, Multi-dimensional data model, Warehouse schema. Data Marts [4L] : Data marts, types of data marts, loading a data mart, metadata, data model, maintenance, nature of data, software components; external data, reference data, performance issues, monitoring requirements and security in a data mart. Online Analytical Processing [4L] : OLTP and OLAP systems, Data Modeling, LAP tools, State of the market, Arbor Essbase web, Microstrategy DSS web, Brio Technology, star schema for multi dimensional view, snowflake schema; OLAP tools. Developing a Data Warehousing [4L] : Building of a Data Warehousing, Architectural strategies & organizational issues, design considerations, data content, distribution of data, Tools for Data Warehousing Data Mining [4L] : Definitions; KDD(Knowledge Discovery database) versus Data Mining; DBMS versus Data Mining, Data Mining Techniques; Issues and challenges; Applications of Data Warehousing & Data mining in Government. Association Rules [4L] : A priori algorithm, Partition algorithm, Dynamic inset counting algorithm, FP – tree growth algorithm; Generalized association rule. Clustering Techniques [4L] : Clustering paradigm, Partition algorithms, CLARA, CLARANS; Hierarchical clustering, DBSCAN, BIRCH, CURE; Categorical clustering, STIRR, ROCK, CACTUS. Decision Trees [4L] : Tree construction principle, Best split, Splitting indices, Splitting criteria, Decision tree construction with presorting. Web Mining [4L] : Web content Mining, Web structure Mining, Web usage Mining, Text Mining. Temporal and Spatial Data Mining [5L] : Basic concepts of temporal data Mining, The GSP algorithm, SPADE, SPIRIT, WUM. ROBOTICS (EC 7114) Robot Anatomy Arm Geometry-Direct & Inverse Kinematics Problem.Arm Dynamics,D Alembert Equations of Motion, Synthesis of elements with movalulity constraints,manipulations-trajectory planning,joint interpolated trajectories. [15L] Control of Robot Manipulation-computed torque technique sequencing & adaptive control, resolved motion control Moluie Robots. [6L] Robot sensing-Range & Proximity & Higher-Level vision, illumination techniques,Imaging Geometry, Segmentation Recognition & Interpretation. [8L] Robot Programming Language Characteristics of Robot Level & Task Level languages.Robot intelligence-State Space search, Robot learning,Robot Task Planning,Knowledge Engineering. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING (EC 7115) 4 Digital image fundamentals: - Image digitization 1L Sampling & quantisation 1L Image resolution 1L Colour perception & processing 1L Image processing: - Pixel based transformation 1L Geometric transformation 1L Local processing: - Edge detection, subpixel location estimation Restoration: - Degradation, inverse fitting, Wiener filtering 1L Binary image processing: - Thresholding, run length encoding 2L Distance transforms, Medial axis transforms 2L Morphological operations 1L Region segmentation & Representation: - Split & merge algorithm 1L Region growing 1L Image filtering: - Histogram modification 1L Linear & Gaussian filters 2L Contours: - Digital curves 3L Poly line splitting 2L Hop along algorithm 2L Conic & Splines Hough transform 2L Fourier description 2L Textures: - Statistical syntactic & model based methods 2L Image transforms: - Fourier, Hadamard, Discrete Cosine 2L Wavelets & other orthogonal transforms 2L Compression of image: - Predictive compression methods, vector quantisation, hierarchical & progressive methods, JPEG, MPEG 3L Case studies 3L MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGY(IT 7107) Introduction to Multimedia: Concepts, uses of multimedia, hypertext and hypermedia.; Image, video and audio standards. [ 8 L ] Audio: digital audio, MIDI, processing sound, sampling, compression. [6 L ] Video: MPEG compression standards, compression through spatial and temporal redundancy, inter-frame and intra-frame compression . [ 8 L ] Animation: types, techniques, key frame animation, utility, morphing. [ 6 L ] Virtual Reality concepts. [ 2 L ] Windows concepts and terminology, key elements Creating the look, communication via messages, windows resources and functions, adding multimedia and sound resources. Writing windows applications, taking control of windows, adding menus, dialog boxes, DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (EC 7110) Introduction, Overview of digital signal processing. 2 L Discrete – Time linear system, Sequences, arbitrary sequences, linear time invariant system, causality, stability. Difference equation, relation between continuous and discrete system. Classifications of sequence, recursive and non-recursive system. 8 L Mathematical operations on sequences: Convolution, graphical and analytical techniques, overlap and add methods, matrix method, some examples and solutions of LTI systems, MATLAB examples (Tutorial) 4 L Z-transform: Definition, relation between Z transform and Fourier transform of a sequence, properties of Z transform, mapping between S-plane and Z-plane. Unit circle, convergence and ROC, Inverse z-transform, solution of difference equation using the one sided Z-transform MATLAB examples (Tutorial). 6 L Discrete Fourier transform: Definition, inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) Twiddle factor, linear transformation, basic properties, circular convolution, multiplication of DFT, linear filtering using DFT, filtering of long data sequences, overlap add and save method. Computation of DFT, Fast Fourier transform (FFT), FFT algorithm, Radix 2 algorithm. Decimation-in-time and decimation-in- frequency algorithm, signal flow graph, butterflies, Chirp z-transform algorithm, MATLAB examples (Tutorial). 1 0 L Digital filter realization: Principle of digital filter realization, structures of All-zero filters. Design of FIR (Finite impulse response) filters, linear phase, windows-rectangular, Berlitt, Hanning, Hamming and Blackman. Design of infinite impulse response filters (IIR) from analog filters. Bilinear transformation, Butterworth, Chebyshev, Elliptic filters. Optimisation method of IIR filters. Some example of practical filter design. Computer aided filter design, MATLAB examples (Tutorial). 1 0 L BIOMEDICAL ELECTRONICS (EC 7116) Origin of bio-potential: Electric activity of excitable cells, resting potential, action potential, Nerst equation, propagation of action potential. Surface map of bio-potential- concept. 3L Biomedical electrodes: Electrode theory. Working principle & application of different bio-potential electrodes & biochemical transducerso Microelectrodes, surface electrodes, needle electrodes o Reference electrode, pH electrode, blood gas electrode 4L o Ion electrode. Cardiovascular measurements: Brief description of cardiovascular system. Electrocardiographyo Sources of cardiac bio-potentials, o Methodology & principle of measurement o Electrocardiograms & their inferences Vector cardiography- concept Principles of direct & indirect measurement of blood pressure Principles of measurement of blood flow/cardiac rate PH & blood gas analyzer 8L Electroencephalography (EEG): Sources of action potentials Methodology & principle of measurement Electroencephalograms & their inferences 4L Electromyography: Sources of action potentials Methodology & principle of measurement Electromyograms & their inferences 4L Respiratory system measurement: Respiratory mechanism, parameters of respiratory system Principle of measurement of various parameters, impedance pneumograph, Spiro meter. 4L Medical imaging systems: Working principles of medical X-ray, CT scan, CAT scan, Ultrasound scanning, MRI 4L Therapeutic & prosthetic devices: Pacemakers, Defibrillators, ventilators, respirators, heamodialysis machine 4L Medical application of LASER including safety aspects 2L Fiber optic application in imaging internal organs 1L Effect of mm wave and microwave on human body 1L Electrical safety: Physiological effect of electricity, micro shock & macro shock hazards, electrical safety standards for human body, basic approaches to shock protection. 1L OPERATIONS RESEARCH AND OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES (EC 7117) Introduction [2L] Introduction to OR modeling approach and various real life situations Linear programming problems [2L] Basic LPP and applications, Various components of LP problem formulation Solving Linear Programming problem [17L] Solving LPP using simultaneous equations and Graphical Method (2L) Simplex Method and extensions. (7L) Sensitivity analysis , Duality theory (2L) Revised Simplex, Transportation and assignment problems. (6L) Network Analysis [7L] Shortest paths, Maximal flow including PERT-CPM Integer programming [2L] Basic concepts, formulation, solution and applications Dynamic programming [4L] Modeling, Optimization, Replacement Game theory [4L] Introduction, Decisions under risk, Decisions under uncertainty Queuing Theory [7L] Introduction, basic definitions and notations, axiomatic derivation of the arrival & departure distributions for Poission Queue, Poission Queuing Model, M/M/1 queues in series, application GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM (CS 7116) Introduction and Overview of Geographic Information Systems [3L Definition of a GIS, features and functions; why GIS is important; how GIS is applied; GIS as an Information System; GIS and cartography; contributing and allied disciplines; GIS data feeds; historical development of GIS. GIS and Maps, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems [4L Maps and their characteristics (selection, abstraction, scale, etc.); automated cartography versus GIS; map projections; coordinate systems; precision and error. Data Sources, Data Input , Data Quality and Database Concepts [3L Major data feeds to GIS and their characteristics: maps, GPS, images, databases, commercial data; locating and evaluating data; data formats; data quality; metadata. Database concepts and components; flat files; relational database systems; data modeling; views of the database; normalization; databases and GIS. Spatial Analysis [3L Questions a GIS can answer; GIS analytical functions; vector analysis including topological overlay; raster analysis; statistics; integrated spatial analysis. Making Maps [6L Parts of a map; map functions in GIS; map design and map elements; choosing a map type; producing a map formats, plotters and media; online and CD-ROM distribution; interactive maps and the Web. Implementing a GIS [4L Planning a GIS; requirements; pilot projects; case studies; data management; personnel and skill sets; costs and benefits; selecting a GIS package; professional GIS packages; desktop GIS; embedded GIS; public domain and low-cost packages. Technology & Instruments involved in GIS & Remote Sensing [8L] GIS applications; GIS application areas and user segments; creating custom GIS software applications; user interfaces; case studies. Future data; future hardware; future software; Object-oriented concepts and GIS; future issues – data ownership, privacy, education; GIS career options and how to pursue them. Remote Sensing [8L Remote sensing of environment, E.M. Principle, Thermal infrared remote sensing, Remote sensing of Vegetation, Remote sensing of water, urban landscape SEMESTER-VIII E-COMMERCE & SECURITY(CS 8117) Introduction to E-Commerce [6L]: Definition, Scope of E-Commerce, Hardware requirements, E-Commerce and Trade Cycle, Electronic Markets, Electronic Data Interchange and Internet Commerce. Business to Business E-Commerce [7L]: Electronic Markets, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): Technology, Standards (UN/EDIFACT), Communications, Implementations, Agreements, Security, EDI and Business, Inter-Organizational E-commerce. Legal issues [5L]: Risks: Paper Document vs. Electronic document, Authentication of Electronic document, Laws, Legal issues for Internet Commerce: Trademarks and Domain names, Copyright, Jurisdiction issues, Service provider liability, Enforceable online contract. Security Issues [6L]: Security Solutions: Symmetric and Asymmetric Cryptosystems, RSA, DES, and Digital Signature, Protocols for secure messaging, Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Protocol, Electronic cash over internet, Internet Security. Business to Consumer E-Commerce [8L]: Consumer trade transaction, Internet, Page on the Web, Elements of E-Commerce with VB, ASP, SQL. E-business [7L]: Internet bookshops, Software supplies and support, Electronic Newspapers, Internet Banking, Virtual Auctions, Online Share Dealing, Gambling on the net, E-Diversity, Case studies through internet. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT & ACCOUNTING (CS 8118) Introduction [3L] Financial Management, Financial Planning and Capitalization- definitions, objectives, changing roles and functions, Financial Decision. Capital Budgeting [7L] Nature of Investment decision, Importance of Capital Budgeting, The Capital. Budgeting Process - Investment Criterion, Pay-back period, Accounting, ROR (Rate of Return) Method, Discounting Cash flow method, Net – present value method, IRR (Internal Rate of Return) method, The benefit-Cost Ratio method. Management of Working Capital [7L] Various concepts, Elements, Classification, Financing and importance of working capital, Investment analysis, Cash flow determination, cost of capital, capital budgeting methods. Budgeting Control Technique [5L] Concepts of Budget, budgeting and budgetary control, Objectives, Functions, Uses, Advantages, Limitations; Master Budget and Report. Cost – Volume – Profit Analysis [8L] Classification of costs, Allocation, apportionment and absorption, Cost centers, different costing systems, Cost analysis for managerial decisions, Meaning of Linear CVP analysis, Objectives, Assumptions, Break – Even analysis, determining the Break-Even point profit, Volume graph profit, Volume ratios margin of Safety. Introduction to Accounting [8L] Basic accounting concepts, important definitions, uses, limitations, advantages; types of Accounting, Financial statements, introduction to Journal Accounting; different types of Vouchers, double entry bookkeeping, different types of transactions related to Financial Accounting. Financial Control [7L] Posting of Ledgers and preparation of Trial Balance; preparation of Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Accounts; Controlling other departments by Financial Accounting (A practical Approach). ELECTIVES III, IV & V NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING (CS 8119) Introduction to NLP [2L]: Definition, issues and strategies, application domain, tools for NLP, Linguistic organisation of NLP, NLP vs PLP. Word Classes [13L]: Review of Regular Expressions, CFG and different parsing techniques 1L Morphology: Inflectional, derivational, parsing and parsing with FST, Combinational Rules 3L Phonology: Speech sounds, phonetic transcription, phoneme and phonological rules, optimality theory, machine learning of phonological rules, phonological aspects of prosody and speech synthesis. 4L Pronunciation, Spelling and N-grams: Spelling errors, detection and elimination using probabilistic models, pronunciation variation (lexical, allophonic, dialect), decision tree model, counting words in Corpora, simple N-grams, smoothing (Add One, Written-Bell, Good-Turing), N-grams for spelling and pronunciation. 5L Syntax [7L]: POS Tagging: Tagsets, concept of HMM tagger, rule based and stochastic POST, algorithm for HMM tagging, transformation based tagging 4L Sentence level construction & unification: Noun phrase, co-ordination, sub-categorization, concept of feature structure and unification. 3L Semantics [9L]: Representing Meaning: Unambiguous representation, canonical form, expressiveness, meaning structure of language, basics of FOPC 2L Semantic Analysis: Syntax driven, attachment & integration, robustness 2L Lexical Semantics: Lexemes (homonymy, polysemy, synonymy, hyponymy), WordNet, internal structure of words, metaphor and metonymy and their computational approaches 3L Word Sense Disambiguation: Selectional restriction based, machine learning based and dictionary based approaches. 2L Pragmatics[8L]: Discourse: Reference resolution and phenomena, syntactic and semantic constraints on Coreference, pronoun resolution algorithm, text coherence, discourse structure 4L Dialogues: Turns and utterances, grounding, dialogue acts and structures 1L Natural Language Generation: Introduction to language generation, architecture, dicourse planning (text schemata, rhetorical relations). MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM(IT 7106) 1. Introduction(2L) Definition of management, its definition, purpose, elements of science, patterns of management analysis. Functions of managers. 2. People & organization. (6L) People: psychological factors, worker’s skill & abilities. Organization:Organizational characteristics, Organizational behavior, corporate culture, power inter-group conflict, intra-group dynamics, the MIS function in organization, MIS personal, computer operation personal, MIS management. 3. System & models. (6L) System: components of a system, environment, open Vs Closed systems. Models: modeling systems general vs specific models, levels of models, types of models. Models of organizational systems. A general model of organization and its internal environment. Strategic planning models. 4. Management & decision making (5L) Management: labels of management, managerial role, planning & control, Managerial styles, Managerial decision making: characteristics of types of decision 5. Decision making process. (3L) Intelligence, design, soln evaluation & choice. 6. Evaluating decision making.(2L) Effectiveness vs efficiency 7. Transaction processing & management reporting systems.(5L) A management information systems frame work: ----- Transaction processing framework ----- Management reporting system ----- Decision support system. ----- Knowledge based systems ----- Office systems 8. Transaction processing.(2L) nature function role of IT in transaction processing processing cycles Transaction processing subsystem. 9. Management reporting system. (2L) Evaluation of management reporting system, types of reports, structuring report content. 10. Decision support system (DSS). (3L) Component of DSS DSS development DSS products DSS development tools User interfaces Executive information system (EIS) Executive roles & decision making. Executive decision making environment 11. MIS in the functional areas of business. (3L) Financial information system, Marketing MIS Manufacturing MIS 12. Enterprise resource planning (3L) Materials Requirement planning (MRP) Closed loop MRP Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP – II) ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING Functional architecture of ERP Benefits of ERP Business Process Reengineering and ERP ERP implementation 13. Supply chain management (1L) Introduction Definition of SCM Features of SCM SCM Stages 14. Cases in MIS (2L) Case study method Analytical Case Issue Case Written Case Analysis Illustrations ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING (EC 8124) 1. Electronic Commerce : Overview, Definitions, Advantages & Disadvantages of E – Commerce, Threats of E – Commerce, Managerial Prospective, Rules & Regulations For Controlling E – Commerce, Cyber Laws. [ 3 L ] 2. Technologies : Relationship Between E – Commerce & Networking, Different Types of Networking For E – Commerce, Internet, Intranet & Extranet, EDI Systems Wireless Application Protocol : Definition, Hand Held Devices, Mobility & Commerce, Mobile Computing, Wireless Web, Web Security, Infrastructure Requirement For E – Commerce . [ 5L ] 3. Business Models of e – commerce : Model Based On Transaction Type, Model Based On Transaction Party - B2B, B2C, C2B, C2C, E – Governance. [2 L ] 4. E – strategy : Overview, Strategic Methods for developing E – commerce. [2 L ] 5. Four C’s : ( Convergence, Collaborative Computing, Content Management & Call Center ). Convergence : Technological Advances in Convergence – Types, Convergence and its implications, Convergence & Electronic Commerce. Collaborative Computing : Collaborative product development, contract as per CAD, Simultaneous Collaboration, Security. Content Management : Definition of content, Authoring Tools & Content Management, Content – partnership, repositories, convergence, providers, Web Traffic & Traffic Management ; Content Marketing. Call Center : Definition, Need, Tasks Handled, Mode of Operation, Equipment , Strength & Weaknesses of Call Center, Customer Premises Equipment (CPE). [ 6 L ] 6. Supply Chain Management : E – logistics, Supply Chain Portal, Supply Chain Planning Tools (SCP Tools), Supply Chain Execution (SCE), SCE - Framework, Internet’s effect on Supply Chain Power. [ 3 L ] 7. E – Payment Mechanism : Payment through card system, E – Cheque, E – Cash, E – Payment Threats & Protections. 8. E – Marketing :. Home –shopping, E-Marketing, Tele-marketing [[[[[[[[ 9. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) : Meaning, Benefits, Concepts, Application, EDI Model, Protocols (UN EDI FACT / GTDI, ANSI X – 12), Data Encryption (DES / RSA). [2 L ] 10. Risk of E – Commerce : Overview, Security for E – Commerce, Security Standards, Firewall, Cryptography, Key Management, Password Systems, Digital certificates, Digital signatures. [4 L ] 11. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Features, capabilities and Overview of Commercial Software, re-engineering work processes for IT applications, Business Process Redesign, Knowledge engineering and data warehouse . Business Modules: Finance, Manufacturing (Production), Human Resources, Plant Maintenance, Materials Management, QualityManagement, Sales&Distribution ERPPackage, ERP Market: ERP Market Place, SAP AG, PeopleSoft, BAAN, JD Edwards, Oracle Corporation ERP-Present and Future: Enterprise Application Integration (EAI), ERP and E-Commerce, ERP and Internet, Future Directions in ERP WIRELESS COMMUNICATION (EC 7112) Introduction to Wireless Communication Systems – evolution of mobile radio communications, mobile radio systems around the world, radio communication systems – paging systems, cordless telephone systems, cellular telephone systems; comparison of common wireless communications, trends in cellular radio and personal communication, second generation (2G) cellular networks, third generation (3G) wireless networks, introduction to radio wave propagation, free space propagation model 10L Basics of mobile communication – Limitations of conventional mobile system, mobile cellular communication – introduction, concept of frequency reuse, cluster size, cellular system architecture – mobile station, base station, MSC, channel assignment strategies, call handover strategies, interference and system capacity, improving capacity in cellular systems – cell splitting, sectoring, repeaters, microcell zone concept. 12L Global system for mobile communication – GSM services and features, system architecture, GSM radio subsystem, GSM channel types, location updating and call setup, introduction to CDMA digital cellular standard, comparison between GSM and CDMA. 10L Wireless networking – wireless local area network standards, technology – RF and IR wireless LAN, diffuse, quasi-diffuse and point-to-point IR wireless LAN, advantages and applications of Wireless LAN, introduction to WI-FI, Bluetooth, 3G and 4G wireless systems 8L [[ FIBER NETWORKS (EC 8125) : 4 Introduction: - Basics of Optical bench, Fibre–end preparation of fibre ends, launching mechanism of light into fibre end, coupling of light into detector. 4L Measuring Instruments: - Lock-in-Amplifier, Monochromator, Infrared viewer, Optical Spectrum Analyser, OTDR. 2L Multi-mode fibre: – Parameters for characterisation, Steady-State Power distribution, mode stripper. 2L Measurements of attenuation: - Loss Mechanisms in Fibre, Calorimetric Method, Absorption & Scattering losses, Differential mode attenuation, Cut-Back method, OTDR techniques; Numerical Aperture- trigonometric & Scanning methods. 8L Refractive Index Profile: - Reflection method, Near Field Scanning, Refracted Near Field methods, Interferometric Slab technique 6L Dispersion Measurements: - Time-Domain Method & Frequency Domain Method 5L Geometrical Measurements: - diameter, deformation, eccentricity, ellipticity. 2L Single–mode Fibre: – Mode Cut-Off wavelength, Mode-field Diameter, Equivalent Step-Index (ESI) Profile, Dispersion, Birefringence Measurement 7L Mechanical Strength of Optical Fibre 2L International Standards for Measurements: World Bodies, RTM, ATM, Recommendations 2L COMPUTER VISION (CS 7118) Discrete geometry & quantization 2L Length estimations 1L Automated visual inspection 2L Object recognition & matching 3L Depth perception problems 2L Stereo geometry & correspondence 4L Motion analysis 3L Optical flow 2L Application of computer vision 4L Remote sensing 4L Bio-medical imaging 4L Document processing 4L Target tracking 4L INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (IT 7108) An Overview on Internet [4L] The need for an Internet, The TCP/IP Internet, Internet services, Internet protocols and standardization, Review of Network technologies. Internetworking Concepts [6L] Architectural model introduction, Application level interconnection, Network level interconnection, Properties of the Internet, Internet Architecture, Interconnection through IP Gateways or routers, Internet and Intranet. Internet Address [5L] Introduction, Universal identifiers, Three primary classes of IP addresses, Classless IP address, Network and Broadcast addresses, Mapping internet addresses to physical addresses (ARP), ARP protocol format, Transport Gateways and subnet addressing, Multicast addressing. Internet Protocol [6L] Internet Architecture and Philosophy, The concept of unreliable delivery, Connectionless delivery system, The Internet Datagram, Routing direct and indirect delivery, Table driven IP routing, Protocol layering, Reliable stream transport, TCP performance, Bootstrap protocol (BOOTP). Routing [7L] The origin of Gateway routing tables, Original Internet Architecture and Cores, Core Gateways, Automatic route propagation, Vector distance (Bellman-Ford), routing, Gateway to Gateway Protocol (GGP), Autonomous system concept, Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), Interior Gateway Protocol (RIP, OSPF, HELLO), Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Combining RIP, HELLO, and EGP, Routing with partial information. Enterprise Networking [7L] Corporate networking, Broadband at the Metropolitan area level, High speed dedicated WAN services and switched WAN services, ISDN, BISDN and ATM services, Frame relay technology and services, Virtual private network concepts PPTP protocol. Internet Servers [4L] DNS, DHCP Servers, FTP, TELNET, E-Mail Firewall & Networking [6L] Introduction, Implementation of Firewall, Activities of Firewall, Configuration of firewall, Firewalls & SSL, SSL implementation, Bit implementation of SSL, Use of SSL. LINUX PROGRAMMING & SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (CS 8120) Introduction to System Administration [ 4 L ] Essential Administrative Tools. [ 4 L ] Starting and shutdown [ 4L ] User Accounts [ 4 L ] Security [ 4 L] TCP / IP Network Management [ 4L] Getting started in LINUX. [ 2 L ] Linux Data Management [ 4 L ] POSIX Threads [4 L] Pipes, Semaphores, Message Queues, Shared Memory, Sockets [ 2 L ] Tool Command Language [ 2 L ] PERL & CGI. REAL TIME & EMBEDDED SYSTEM (EC 7113) Introduction-defining Real time systems,Embedded Real Time Systems,Special Characteristics of real time systems,a brief evolutionary history. Hardware Architectures of Real Time systems. [12L] Software architectures(concepts of interrupt driven activation,need for real time monitor,pseudo parallelism),meeting of dead lines & real time constraints.[5L] Overview of WARD & MELLOR Methodology: Ward & Mellor Life Cycle,the essential model step,the implementation model,real time extensions of DFD[10L] Real time languages: overview of ADA/Java Extension [4L] Real time Operating Systems . [4L] System Development Methodologies. BIO INFORMATICS (IT 8110) Introduction to Genomic data and Data Organization: Sequence Data Banks – Introduction to sequence date banks – protein sequence data bank. NBFR-PIR, SWISSPROT, Signal peptide data bank, Nucleic acid sequence data bank – GenBank, EMBL nucleotide sequence data bank, AIDS virus sequence data bank. RRNA data bank, structural data banks – protein Data Bank (PDB), The Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) : Genome data bank – Metabolic pathway data : Microbial and Cellular Data Banks. Introduction to MSDN (Microbial Strain Data Network): Numerical Coding Systems of Microbes, Hibridoma Data Bank Structure, Virus Information System Cell line information system; other important Data banks in the area of Biotechnology/life sciences/biodiversity. Sequence analysis: Analysis Tools for Sequence Data Banks; Pair wise alignment - NEEDLEMAN and Wunsch algorithm, Smith Waterman, BLAST, FASTA algorithms to analyze sequence data: Sequence patterns motifs and profiles. Secondary Structure predictions; prediction algorithms; Chao-Fasman algorithm, Hidden- Markov model, Neural Networking. Tertiary Structure predictions; prediction algorithsms; Chao-Fasman algorithm, Hidden- Markov model, Neural Neworking. Applications in Biotechnology: Protein classifications, Fold libraries, Protein structure prediction: Fold recognition (threading), Protein structure predictions : Comparative modeling (Homology), Advanced topics: Protein folding, Protein-ligand interactions, Molecular Modeling & Dynamics, Drug Designing. INFORMATION & CODING THEORY(CS 8121) Source Coding [7L] Uncertainty and information, average mutual information and entropy, information measures for continuous random variables, source coding theorem, Huffman codes. Channel Capacity And Coding [7L] Channel models, channel capacity, channel coding, information capacity theorem, The Shannon limit. Linear And Block Codes For Error Correction [8L] Matrix description of linear block codes, equivalent codes, parity check matrix, decoding of a linear block code, perfect codes, Hamming codes. Cyclic Codes [7L] Polynomials, division algorithm for polynomials, a method for generating cyclic codes, matrix description of cyclic codes, Golay codes. BCH Codes [8L] Primitive elements, minimal polynomials, generator polynomials in terms of minimal polynomials, examples of BCH codes. Convolutional Codes [8L] Tree codes, trellis codes, polynomial description of convolutional codes, distance notions for convolutional codes, the generating function, matrix representation of convolutional codes, decoding of convolutional codes, distance and performance bounds for convolutional codes, examples of convolutional codes, Turbo codes, Turbo decoding. VALUES & ETHICS OF PROFESSION (IT 6105) Science, Technology and Engineering as knowledge and as Social and Professional Activities Effects of Technological Growth: Rapid Technological growth and depletion of resources, Reports of the Club of Rome. Limits of growth: sustainable development Energy Crisis: Renewable Energy Resources Environmental degradation and pollution. Eco-friendly Technologies. Environmental Regulations, Environmental Ethics Appropriate Technology Movement of Schumacher; later developments Technology and developing notions. Problems of Technology transfer, Technology assessment impact analysis. Human Operator in Engineering projects and industries. Problems of man, machine, interaction, Impact of assembly line and automation. Human centered Technology. Ethics of Profession: Engineering profession: Ethical issues in Engineering practice, Conflicts between business demands and professional ideals. Social and ethical responsibilities of Technologists. Codes of professional ethics. Whistle blowing and beyond, Case studies. Profession and Human Values: Values Crisis in contemporary society Nature of values: Value Spectrum of a good life Psychological values: Integrated personality; mental health Societal values: The modern search for a good society, justice, democracy, secularism, rule of law, values in Indian Constitution. Aesthetic values: Perception and enjoyment of beauty, simplicity, clarity Moral and ethical values: Nature of moral judgements; canons of ethics; ethics of virtue; ethics of duty; ethics of responsibility. |
|
#11
2nd November 2012, 06:27 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
your question is quite well confusing....... but making as a random choice that you might be a B. tech student ...... the syllabus is as :
SYLLABUS FOR B.TECH(Bachelor of Technology) STUDENTS : Since its an 8-semesters course , the whole structure(from 3rd sem. to 8th sem.) is as : SEMESTER-III NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND PROGRAMMING (MA 3103) Numerical computation and error, solution of algebraic and transcendental equations- Bisection method, Regula-Falsi method and Newton-Raphson method and their order of convergence. Iterative methods for system of non-linear equations. Linear system of equations: Gauss elimination method, Crout’s method, Jacobi’s method, Gauss-Seidel method. Computer programming of above methods. 16 L Finite differences, difference operators and symbolic relations, difference of a polynomial, Interpolation ,error in interpolation, Newton’s forward and backward formulae, Lagrange’s interpolation formula, Newton general interpolation formula, Numerical differentiation, error in numerical differentiation. Numerical integration: Newton’s cote’s formula, Trapezoidal rule, Simpson 1/3 rule, Simpson 3/8 rule and their error estimation. Computer programming of above methods. 16 L Ordinary differential equations: Taylor’s series method, Euler’s method, Euler’s modified method, Runge-Kutta method, Boundary value problem-linear and non-linear equations. Computer programming of above methods. 10 L MATERIAL SCIENCE (B) (PH 3103) Introduction: - Material Science and Engineering, classification of engineering materials, structure property relationship in materials, introduction to metals & alloys, Ceramics, polymers, composites. 03L Crystal Geometry: Introduction, the space lattices, and lattice points, Unit cell and primitive cell, crystal systems, Bravias lattices, crystal direction and planes, reciprocal lattice, Miller indices, coordination number and atomic packing factor and its determination for simple cubic and Hexagonal closed packed structure. Determination of crystal structure by X – ray diffraction. 07L Crystal Imperfections: Introduction, Classification of imperfection, Point, line and surface imperfection. 03L Phase Diagrams: The phase rule, single component system, Binary phase diagrams, and the lover rule. The iron-iron carbide phase diagram, Hume – Rothrey rules of alloying. Oxidation and Corrosion: Oxidation, mechanism of oxidation, oxidation resistant materials, Corrosion, The principle of corrosion, various forms of corrosion, Protection against corrosion. 04L Diffusion in solids: Introduction, types and mechanism of diffusion, Fick’s law of diffusion, the atomic model of diffusion. Experimental determination of diffusion coefficient, The Kirkendall effect. 05L Dielectrics: Introduction, Dielectric polarization, types of polarization, Temperature and frequency effects, Ferro electricity, and piezoelectricity. 04L Magnetic properties: Diamagnetism, paramagnetism, ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism, soft and hard magnetic materials, magnetic moment due to electron spin 05L Electrical properties : The free electron theory, Fermi- Dirac distribution function, conduction by free electron, Mobility and conductivity, energy band theory of solids, Insulators, semiconductors, metals, potential field in a metal, bond and free electron, Superconductivity and superconducting materials, Type I and Type II superconductors, The Meissner’s effect. MATHEMATICS – III (MA 3104) LAPLACE TRANSFORMATION :- Definition of Laplace transform and linearity and shifting property, Laplace transform of elementary functions, Inverse Laplace transform, Laplace transform of derivative and integration, convolution theorem, Solution of differential equation by Laplace transform, Unit Step function, Unit impulse function. 09 L VECTOR CALCULUS :- Differentiation of vector function, gradient, divergence, curl and their geometrical or physical interpretation, Line, Surface and Volume integrals, Statement of Green’s Theorem , divergence theorem and Stoke’s theorem and their applications. Curvilinear co-ordinates. 09 L FOURIER SERIES :- Fourier series, Dirichlet’s conditions, Half Range series. 04 L FOURIER TRANSFORM :- Definition of Fourier Transform, linearity, shifting, frequency theorem, Fourier transform of derivatives and Dirac-delta function, Inverse Fourier transform, Fourier Sine and Cosine transform, Solution of simple differential equation by Fourier transform method. 10 L Z- TRANSFORMATION :- Definition, Z-transformation of standard sequences, linearity property, Shifting theorem, inverse of Z-transformations, Scaling property of Ztransformation, differentiation of Z-transformation, convolution of sequences, solution of difference equations by Z-transformation. DATA STRUCTURE (CS 3101) Overview of C language [ 6 L ] Time and Space analysis of Algorithms - Order Notations. Linear Data Structures - Sequential representations - Arrays and Lists, Stacks, Queues and Dequeues, strings, Application. [ 6 L ] Linear Data Structures, Link Representation - Linear linked lists, Circularly linked lists. Doubly linked lists, application. [ 6 L ] Recursion - Design of recursive algorithms, Tail Recursion, When not to use recursion, Removal of recursion. [ 4 L ] Non-linear Data Structure: Trees - Binary Trees, Traversals and Threads, Binary Search Trees, Insertion and Deletion algorithms, Height-balanced and weight-balanced trees, Btrees, B+ -trees, Application of trees; Graphs - Representations, Breadth-first and Depth-first Search. [10 L ] Hashing - Hashing Functions, collision Resolution Techniques. [ 4L] Sorting and Searching Algorithms- Bubble sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort, Quick Sort, Merge Sort, Heap sort and Radix Sort. [ 6 L ] File Structures - Sequential and Direct Access. Relative Files, Indexed Files - B+ tree as index. Multi-indexed Files, Inverted Files, Hashed Files. DIGITAL ELECTRONICS & INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (EC 3102) Number systems, Binary representation, Codes and their conversions: BCD, Octal, Hexadecimal, ASCII, EBDIC, Gray, Signed binary number representation with 1’s and 2’s complement methods, Binary arithmetic. 5L Boolean algebra, Venn diagram, logic gates and circuits, Minimization of logic expressions by algebraic method, K-map method and Quine Mc Clauskey method 8L Combinational circuits- adder, subtractor, encoder, decoder, comparator, multiplexer, de-multiplexer, parity generator. 6L Design of combinational circuits-Programming logic devices and gate arrays. 2L Sequential Circuits- Flip Flops, various types of Registers and counters and their design, Irregular counter, State table and state transition diagram, sequential circuits design methodology 8L Different types of A/D and D/A conversion techniques. 5L Different Logic families- TTL, ECL, MOS and CMOS, their operation and specifications. 4L Memory Systems: RAM, ROM, EPROM,EEROM 2L PRINCIPLE OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES (IT 3102) Concepts of structural program development; concept of data types; precedence and associativity of operators; conditional transfer; deterministic and in-deterministic loops; Recursions; functions and procedures - call by value, call by reference and their differences; programming for numerical methods; records. Data-type handling and various constructs (conditional, loop, functions etc); pointers: concept of pointers and passing parameters using pointers, non-numeric processing, concept of arrays of pointers and pointers to pointers; [8 L ] structures and unions – advantage of using structures, concept of information hiding, pointers to structures; files - basic concept of various types of file access methods: sequential, indexed sequential, random, various statements for file handling [ 8 L ] Advanced Programming Languages like C++, ADA, LISP, PROLOG, and PASCAL. Comparison of various languages SEMESTER-IV MATHEMATICS – IV (MA 4105) SPECIAL FUNCTIONS :- Series solution of differential equations, Bessel and Legendre’s equations and their series solution, elementary properties of Bessel’s function and Legendre’s polynomial. 12 L COMPLEX VARIABLE:- Analytic function, Cauchy- Riemann equation. Complex Integration, Cauchy’s theorem and Cauchy Integral formula. Taylor and Laurent’s expansion. Poles and Residue, Residue theorem. Conformal transformation, Bilinear and Schwartz’s transformations. . 15 L PARATIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION :- Formulation of partial differential equation, Linear and non-linear partial differential equations of the first order, Lagrange’s method and Charpit’s method. Higher order Partial Linear differential equations with constant coefficients. Method of separation of variables. Equation of vibrating strings, heat flow, Laplace’s two dimensional equation and simple problems. PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS (MA 4106) Probability: classical and axiomatic definitions, addition law, conditional probability, multiplication law, total probability, Baye’s theorem and independence of events. Random variables: Discrete and continuous random variables, probability mass, probability density and commutative distribution functions. Mathematical expectation, variance, moment and moment generating function, Chebyshev ‘s inequality.10 L Regression Analysis: Linear regression, principle of least square, non-linear regression, correlation, coefficient of correlation, Rank correlation. 05 L Distributions: Binomial, Hypergeometric, Geometric, Poisson and Normal distributions. Sampling Distribution: Population samples, sampling distribution, estimate for population mean and variance, point of estimation, confidence interval for mean and variance of normal population, Testing of hypothesis, the critical and acceptance region, two type of errors, Chi-square, t-student and F distributions. 12 L Analysis of Variance: completely randomize design and randomized block design, Quality control, control charts(X-chart, R-chart, P-chart and C-chart). ANALOG ELECTRONICS (EC 4103) Transistor Biasing and Stability: Self Bias-CE, CC, Compensation techniques. Voltage, current, transresistance & transconductance amplifier. 6L High frequency model of transistor. 2L Power amplifiers – Class A, B, AB, C, Tuned amplifier.Push –pull amplifiers. 6L Operational Amplifier: Differential Amplifier using BJT and FET,Internal structuer of Op-amp, C onstant current source (current mirror etc.), level shifter, Ideal and practical OpAmp. Comparator, Schmitt Trigger. Instrumentation Amplifier, Log & Anti-log amplifiers, Trans-conductance multiplier,Linear &Nonlinear Precision Rectifier 10L Multivibrator – Monostable, Bistable, Astable.Ckts & Timer. Monostable and astable operation using 555 timer. 6L Linear voltage regulator : series and shunt. Switched mode power supply. 4L Function generator, wave shapers. V-I, I-V, V-F & F-V converters. VCO, PLL lock-in amplifier. 6L COMMUNICATION SYSTEM & ENGG. (EC 4104) 1. 1. Wave spectra: Introduction, spectral analysis of respective waves. 2. Noise: Introduction, Thermal noise, S/N ratio, Equivalent Noise Resistance, Noise Factor, Noise Temperature. 3. Modulation and demodulation of signals: (i) Amplitude Modulation, Frequency spectrum, Average power, Diode envelope detection. (ii) SSB modulation, Principles, FET Balanced Modulators, SSB Generation by Phase shift method. (iii) FM and PM: Frequency spectra, Equivalence between FM and PM, FET Reactance Modulator, The Armstrong method, FM stereo Broad Transmitter, Foster seely Discriminator, Pre-emphasis and De-emphasis. Automatic Frequency control. 4. Performance of Communication Systems. Noise in Amplitude Modulated systems and Angle modulated systems. 5. Super heterodyne Receivers (Block diagram treatment) choice of IF and Oscillator frequency, Image rejection. 6. Sampling Theorem, Pulse Modulation, Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Time Modulation, TDM, FDM. 7. Digital Communication: Pulse code modulation, Delta Modulation, Quantization Noise in Binary PCM, Digital carrier systems: ASK, FSK, PSK, and DPSK. 8. Introduction to Information theory, Measure of information channel capacity, exchange of BW for S/N ratio. MICROPROCESSOR AND INTERFACING (EE 4107) Introduction to 8085A CPU architecture-register organization, addressing modes and their features. Software instruction set and Assembly Language Programming. Pin description and features. Instruction cycle, machine cycle, Timing diagram. Hardware Interfacing: Interfacing memory, peripheral chips (IO mapped IO & Memory mapped IO). Interrupts and DMA. Peripherals: 8279, 8255, 8251, 8253, 8237, 8259, A/D and D/A converters and interfacing of the same. Typical applications of a microprocessor. 16 bit processors: 8086 and architecture, segmented memory has cycles, read/write cycle in min/max mode. Reset operation, wait state, Halt state, Hold state, Lock operation, interrupt processing. Addressing modes and their features. Software instruction set (including specific instructions like string instructions, repeat, segment override, lock prefizers and their use) and Assembly Language programming with the same. Brief overview of some other microprocessors (eg. 6800 Microprocessor). SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (CS 4102) Software Quality [12L] Software Quality Assurance, Software Metrics, Software Validation, Static and Dynamic Analysis, Symbolic Equation, Mutation Analysis, Dynamic Testing, Unit Testing, White-box and Black-box Testing, Test Case Generation, Integration Testing, Bottom-up and Top-down Testing, System Testing, Function Testing, Performance Testing, Acceptance Testing, Installation Testing, Theoretical Foundation of Testing, Formal Verification, Test tools. User Interface [10L] Module Introduction, Objectives of Usability, How to Approach Usability, Designing with Usability in mind, Measuring Usability, Guidelines for User Interface Design, User Interface Elements, Dialog Design, SSADM, Methodology for Dialog Design, Prototyping Tools. Software Reliability [10L] Reliability, Hazard, MTTF, Repair and Availability, Steady-State Availability, Estimation of Residual Errors, Reliability Models, Software Complexity, Cyclomatic Complexity, Halstead’s Metrics. Project Management [12L] Issues in Project Management, Management Functions, Software Project Management Plan, Software Management Structure, Personnel Productivity, Software Project Complexity, Software Metrics – Basic Consideration, Size Oriented and Function Point Oriented; Software Cost Estimation Techniques, Algorithmic Cost Modeling, The COCOMO Model, Project Scheduling, Software Project Planning, Scheduling Risk Management. SEMESTER-V OPERATING SYSTEMS (CS 5103) Introduction [4L] Introduction to OS. Operating system functions, evaluation of O.S., Different types of O.S.: batch, multi-programmed, time-sharing, real-time, distributed, parallel. System Structure[3L] Computer system operation, I/O structure, storage structure, storage hierarchy, different types of protections, operating system structure (simple, layered, virtual machine), O/S services, system calls. Process Management [17L] Processes [3L]: Concept of processes, process scheduling, operations on processes, cooperating processes, inter-process communication. Threads [2L]: overview, benefits of threads, user and kernel threads. CPU scheduling [3L]: scheduling criteria, preemptive & non-preemptive scheduling, scheduling algorithms (FCFS, SJF, RR, priority), algorithm evaluation, multi-processor scheduling. Process Synchronization [5L]: background, critical section problem, critical region, synchronization hardware, classical problems of synchronization, semaphores. Deadlocks [4L]: system model, deadlock characterization, methods for handling deadlocks, deadlock prevention, deadlock avoidance, deadlock detection, recovery from deadlock. Storage Management [19L] Memory Management [5L]: background, logical vs. physical address space, swapping, contiguous memory allocation, paging, segmentation, segmentation with paging. Virtual Memory [3L]: background, demand paging, performance, page replacement, page replacement algorithms (FCFS, LRU), allocation of frames, thrashing. File Systems [4L]: file concept, access methods, directory structure, file system structure, allocation methods (contiguous, linked, indexed), free-space management (bit vector, linked list, grouping), directory implementation (linear list, hash table), efficiency & performance. I/O Management [4L]: I/O hardware, polling, interrupts, DMA, application I/O interface (block and character devices, network devices, clocks and timers, blocking and nonblocking I/O), kernel I/O subsystem (scheduling, buffering, caching, spooling and device reservation, error handling), performance. Disk Management [3L]: disk structure, disk scheduling (FCFS, SSTF, SCAN,C-SCAN) , disk reliability, disk formatting, boot block, bad blocks. Protection & Security [4L] Goals of protection, domain of protection, security problem, authentication, one time password, program threats, system threats, threat monitoring, encryption. DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (CS 5104) Introduction [3L] File & Data Base Concept, Overview of DBMS, Data Models, Database Administrator, Database Users, Schema. Data Independence Entity-Relationship Model [3L] Basic concepts , Keys, Entity-Relationship Diagram, Cardinality ratios, Strong & Weak Entity Sets, Specialization, Generalization, Aggregation. Relational Model [4L] Procedural & Non Procedural Languages, Relational Algebra, Extended Relational Algebra Operations, Views, Modifications Of the Database, Relational Calculus . SQL [5L] Basic Concepts, Set operations, Aggregate Functions, Null Values, assertions, views, Nested Sub-queries, Cursors, Stored procedures and triggers. Integrity Constraints & Introduction to RDBMS [3L] Domain Constraints, Referential Integrity Constraints, Codd’s rule. Functional Dependencies and Normalization [7L] Functional Dependency, Armstrong’s axioms, Canonical Cover, Closure , Full and Partial Functional dependencies, Prime & Non Prime attribute , 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, Multi valued Dependency , 4NF, 5NF, DKNF . Transaction & Concurrency Control [5L] Transaction concept, ACID properties, Conflict & View serializabilty, Test for Conflict serializability, Concurrency Control, Lock base protocols, Two phase locking. Storage Strategies [4L] Single-Level Index (primary, secondary, clustering), Multi-level Indexes, Dynamic Multilevel Indexes, Hashing Techniques, B tree and B+ tree . Query Optimization [4L] Full Table scan, Indexed-based scan, Merge join, Nested loop join , Equivalence rules , Heuristic Optimization , Cost Based Optimization. Backup & Recovery [3L] Physical & Logical Backup , Transaction logs, Causes of failures , Recovery techniques. Distributed Databases [4L] Basic Concepts, Data Fragmentation, Replication and Allocation Techniques, Types of Distributed Database Systems, Query Processing, Overview of Client-Server Architecture and Its relationship to Distributed Databases. DESIGN & ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS (CS 5105) Models of computation [4L]: Random Access Machine, Relationship between Turing Machine and RAM, Time and Space Complexity. Complexity analysis [8L]: Asymptotic notations, Recurrence for divide and conquer and its solution, Merge sort, Heap sort, Quick sort and their complexity. Dynamic Programming [4L]: Basic method, Matrix-chain multiplication, All pair shortest paths, Single-source shortest path, Travelling Salesman problem. Greedy Method [5L]: Basic method, Knapsack problem, Job sequencing with deadlines, Minimum spanning tree by Prim's and Kruskal's algorithms. Disjoint Set Manipulation [4L]: Set manipulation algorithm like UNION-FIND, Union by rank, Path compression. Graph Traversal Algorithms [5L]: BFS and DFS, Backtracking and its use in solving Knapsack and Eight queens problem. Matrix Manipulation Algorithms [6L]: Strassen’s Matrix-multiplication algorithm and its applications in Solution of simultaneous linear equations using LUP decomposition, Inversion of Matrix and Boolean Matrix multiplication. Notion of NP-completeness [5L]: P class, NP-hard class, NP-complete class, Circuit Satisfiability problem. Approximation Algorithms [4L]: Vertex cover problem, Travelling salesman problem, Set covering problem. COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE (CS 5106) Concepts & Terminology: Digital computer concepts; Von-Neumann concept ; Hardware & Software and their nature ; structure & functions of a computer system , Role of operating system. [ 8 L ] Memory Unit : Memory classification , characteristics ; Organization of RAM , address decoding ROM/PROM/EEPROM ; Magnetic memories , recording formats & methods , Disk & tape units; Concept of memory map , memory hierarchy , Associative memory organization ; Cache introduction , techniques to reduce cache misses , concept of virtual memory & paging. [ 8 L ] CPU Design: The ALU – ALU organization , Integer representation , 1s and 2s complement arithmetic ; Serial & Parallel Address; implementation of high speed Address Carry Look Ahead & carry Save Address; Multiplication of signed binary numbers-Booth’s algorithm ; Divide algorithms- Restoring & Non-Restoring ; Floating point number arithmetic; Overflow detection , status flags. [ 8 L ] Instruction Set Architecture- Choice of instruction set ; Instruction word formats ; Addressing modes. [ 5 L ] Control Design – Timing diagrams; T-States , Controlling arithmetic & logic instruction , control structures ; Hardwired & Micro programmed, CISC & RISC characteristics. [ 6 L ] Pipelining - General concept , speed up , instruction & arithmetic pipeline; Examples of some pipeline in modern processors , pipeline hazards; Flynn’s classification –SISD ,SIMD , MISD , MIMD architectures-Vector and Array processors & their comparison , Concept of Multiprocessor; Centralized & distributed architectures. [ Input/output Organization : Introduction to Bus architecture , effect of bus widths , Programmed & Interrupt I/O , DMA. FORMAL LANGUAGES & AUTOMATA THEORY(CS 5107) Finite State Machines [4L] Definition, concept of sequential circuits, state table & state assignments, concept of synchronous, asynchronous and liner sequential machines Finite State Models [10L] Basic definition, mathematical representation, Moore versus Mealy m/c, capability & limitations of FSM, state equivalence & minimization, machine equivalence, incompletely specified machines, merger graph & compatibility graph, merger table, Finite memory, definite, information lossless & inverse machines : testing table & testing graph. Structure of Sequential Machines [3L] Concept of partitions, closed partitions, lattice of closed partitions, decomposition : serial & parallel. Finite Automation [9L] Preliminaries (strings, alphabets & languages, graphs & trees, set & relations), definition, recognition of a language by an automata - idea of grammar, DFA, NFA, equivalence of DFA and NFA, NFA with e-moves, regular sets & regular expressions : equivalence with finite automata, NFA from regular expressions, regular expressions from DFA, two way finite automata equivalence with one way, equivalence of Moore & Mealy machines, applications of finite automata. Closure Properties of Regular Sets [4L] Pumping lemma & its application, closure properties minimization of finite automata : minimization by distinguishable pair, myhill-nerode theorem. Context Free Grammars [4L] Introduction, definition, derivation trees, simplification, CNF & GNF. Pushdown Automata [5L] Definition, moves, instantaneous descriptions, language recognised by PDA, deterministic PDA, acceptance by final state & empty stack, equivalence of PDA and CFL. Closure Properties of CFLs [4L] Pumping lemma & its applications, ogden’s lemma, closure properties, decision algorithms. Introduction to ZRL & CSL [2L] Introduction to Z. Regular language properties and their grammars, Context sensitive languages. SEMESTER-VI INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT (ME 6123) Human Resource Management: [8L] Recruitment and selection, Performance appraisal, Industrial Relations, Trade Union, Collective Bargaining Organizational Behaviour: [8L] Different Schools of Management Thought : Scientific Management, Administrative Theory, Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relations Theory(Elton Mayo). Motivation: Concept, Different Theories (Maslow, ERG, Herzberg, ) Communication: Purpose, process, Barriers to effective communication, Guidelines to make communication effective. Perception: Process, Importance, Factors influencing perception, Shortcuts for judging people- Halo effect, Stereotyping, Projection. Quality Management: [6L ] Concept, Dimensions for goods and services, Cost of Quality, Statistical Quality Control, Control Charts, Acceptance Sampling (single). Total Quality Management: Concept, benefits, Criticism. New Quality Tools: Kaizen, Six Sigma, Quality Circles. Productions Management: [ 5L ] Concept. Difference from Operations Management, Types of Production( Mass, Batch, Project), Functions of Production Management. Productivity: Concept, Different Inputs and Productivity Measures, Effeciency and Effectiveness, Measures to increase Productivity. Marketing Management: [6L ] Basic Concepts of Marketing, Difference between Selling and Marketing, Elements of Marketing Mix- the 4 P’s. Marketing Environment: Mega Environment, Micro Environment, Internal Environment, Relevant Environment. Simple Marketing Strategies: SWOT Analysis, BCG Matrix, Industry Matrix. Materials Management: [6L ] Concept, Functions, EOQ Models- Wilson model, model with shortage, model with quantity discount, model without shortage , Selective Inventory Control—ABC, VED, FSN analysis. COMPILER DESIGN (CS 6108) Classification of grammars. Context free grammars. [ 6 L ] Deterministic finite state automata (DFA) Non-DFA Scanners. Top down parsing, LL grammars. Bottom up parsing. Polishing expressions Operator precedence grammar. LR grammars. Comparison of parsing methods. Error handling. [ 20 L ] Symbol table handling techniques. Organisation for non-block and block structured languages. Run time storage administration. [ 6 L ] Static and dynamic allocation. Intermediate forms of source program. Polish N-tuple and syntax trees. [ 4 L ] Semantic analysis and code generation. Code optimisation, folding, and redundant subexpression evaluation. Optimisation within iterative loops. SOFT COMPUTING (CS 6109) Introduction to artificial neural network [ 10L ] Neural Networks: History, overview of biological Neuro-system, Mathematical Models of Neurons, ANN architecture, Learning rules, Learning Paradigms-Supervised, Unsupervised and reinforcement Learning, ANN training Algorithms-perceptions, Training rules, Delta, Back Propagation Algorithm, Multilayer Perceptron Model, Applications of Artificial Neural Networks. Competitive learning networks, Kohonen self organizing networks, Hebbian learning; Hopfield Networks, Associative Memories, The boltzman machine; Applications. Fuzzy Logic [ 12L ] Fuzzy Logic: Introduction to Fuzzy Logic, Classical and Fuzzy Sets: Overview of Classical Sets, Membership Function, Fuzzy rule generation. Operations on Fuzzy Sets: Compliment, Intersections, Unions, Combinations of Operations, Aggregation Operations. Fuzzy Arithmetic: Fuzzy Numbers, Linguistic Variables, Arithmetic Operations on Intervals & Numbers, Lattice of Fuzzy Numbers, Fuzzy Equations.Fuzzy Logic: Classical Logic. Genetic algorithms(Gas),Evolution strategies(Ess),Evolutionary programming(EP),Genetic Programming(GP),Selecting,crossover,mutation,schem a analysis,analysis of selection algorithms;convergence;Markov & other stochastic models. [ 10L ] Other Soft computing approaches [ 7L ] Simulated Annealing, Tabu Search, Ant colony based optimisation, etc. COMPUTER NETWORKS (IT 6103) Overview of Data Communications and Networking [2L] Introduction, Network Models Physical Layer [8L] Signals, Digital Transmission, Analog Transmission, Multiplexing, Transmission Media, Circuit Switching and Telephone Network. Data Link Layer [9L] Error Detection and Correction, Data Link Control and Protocol, Point to Point Access :PPP, Multiple Access, Local Area Networks : Ethernet, Wireless Lans, Connecting Lans, Backbone Networks, Virtual Lans, Cellular Telephone and Satellite Networks, Virtual Circuit Switching. Network Layer [8L] Host-to-Host Delivery :Internetworking, Addressing and Routing, Network Layer Protocols : ARP, IPv4, ICMP, IPv6, and ICMPv6, Unicast and Multicast Routing : Routing Protocols. Transport Layer [5L] Process-to-Process Delivery : UDP and TCP, Congestion Control and Quality of Service. Application Layer [9L] Client-Server Model : Socket Interface, Domain Name System (DNS), Electronic Mail (SMTP), and File Transfer (FTP), HTTP and WWW, Multimedia. Security [4L] Cryptography, Message Security, User Authentication, and Key Management, Security Protocols in the Internet. COMPUTER GRAPHICS (CS 6110) Introduction to Computer Graphics & Graphics Systems [4L] Overview of CG, definitions of CG, types of CG, storage tubes displays, CRT technologies - Raster Scan Display, Computer graphics software. Scan Conversion [6L] Points & lines, Line drawing algorithms; DDA algorithm, Bresenham’s line algorithm, Circle generation algorithm; Ellipse generating algorithm; scan line polygon, fill algorithm, boundary fill algorithm, flood fill algorithm. 2D Transformation [8L] Basic transformations: translation, rotation, scaling; Matrix representations & homogeneous coordinates, transformations between coordinate systems; reflection shear; Transformation of points, lines, parallel lines, intersecting lines. Viewing [4L] Viewing pipeline, Window to Viewport co-ordinate transformation, clipping operations, point clipping, line clipping, clipping circles, polygons & ellipse. 3D Transformation & Viewing [10L] 3D transformations: translation, rotation, scaling & other transformations. Rotation about an arbitrary axis in space; reflection through an arbitrary plane; general parallel projection transformation; clipping, Viewport clipping, 3D viewing, perspectives & Depth Cueing. Curves and Fractals [4L] Curve representation, surfaces, designs, Bezier curves, B-spline curves, end conditions for periodic B-spline curves, rational B-spline curves. Hidden Surfaces [4L] Depth comparison, Z-buffer algorithm, Back face detection, BSP tree method, the Printer’s algorithm, scan-line algorithm; Hidden line elimination, wire frame methods, fractal - geometry. Color & Shading Models [5L] Introduction, Modeling Light Intensities and Sources, Diffuse Reflection, Lambert’s Cosine Law, Specular Reflection, Halftoning, Color Models - RGB Color, CMY Color. SEMESTER - VII VLSI DESIGN (EC 7111) Analog VLSI Circuit Design: - i) Review of MOSFET characteristics, scaling and small-geometry effects, MOSFET capacitances. 3 L ii) MOS resistor, MOS current source, current mirror circuits. MOS voltage source Linear voltage and current converters. 3 L iii) CMOS operational amplifier (OPAMP) design: - Differential amplifier, level shifter, source follower, output stage voltage and power amplifiers. Cascode OPAMP. Compensation techniques. 5 L iv) Analog Filters: - Switched capacitor (SC) fundamentals, first order SC circuits, second-order SC circuits and cascade design. 3 L v) Analog to digital and digital to analog converters, speed of conversion and over sampling issues. 4 L vi) VLSI Interconnects: - distributed RC model, transmission line model. Future inter connect technologies. 2 L Digital VLSI Circuit Design: - i) MOS inverters, CMOS inverter, state characteristics, switching characteristics, power dissipation issues. 3 L ii) CMOS logic gates: NAND, NOR, XOR, CMOS logic design of half and full adders. CMOS transmission gates, pseudo-nMOS, domino logic gates. 5 L iii) Sequential MOS Logic Circuits: The SR latch circuit, clocked latch and flip-flop, CMOS D-latch and edge-triggered circuits, Schmitt trigger circuit, Comparator. 4 L iv) Dynamic Logic Circuits: Pass transistor logic, synchronous dynamic circuit techniques. 3 L v) Semiconductor Memories: ROM circuits, SRAM circuits, DRAM circuits, drivers and buffers, Buffer scaling and design issues. 5 L ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & EXPERT SYSTEM (CS 7111) Introduction [2L] :Overview of AI, Problems of AI, AI techniques; Problem Solving - Problem space and search, Defining the problem as state space search, Problem characteristics; Tic-Tac-Toe problem. AI languages [4L] Basic knowledge of programming languages like Prolog and Lisp. Basic Search Techniques [4L] :Solving problems by searching; Uniform search strategies: breadth first search, depth first search, depth limited search, bidirectional search, comparing search strategies in terms of complexity. Special Search Techniques [6L] : Heuristic Search- greedy best-first search, A* search; Hill climbing search, Simulated annealing search; Genetic algorithms; Constraint satisfaction problems; Adversarial search - Games, Optimal decisions and strategies in games, Minimax search, Alpha-beta pruning. Symbolic Logic [5L] :Syntax and semantics for propositional logic, Syntax and semantics of FOPL, Properties of WFF, Clausal form, Unification, Resolution. Reasoning Under Inconsistencies and Uncertainties [3L] :Non-monotonic reasoning, Truth maintenance systems, Default reasoning & closed world assumption, Predicate completion and circumscription, Fuzzy logic. Probabilistic Reasoning [3L] :Bayesian probabilistic inference, Representation of knowledge in uncertain domain, Semantics of Bayesian networks, Dempster-Shafer theory. Structured Knowledge [4L] ::Associative networks, Conceptual graphs, Frame structures. Expert Systems [4L] :Rule based systems, Nonproduction systems: decision tree architectures, blackboard system architectures, neural network architectures. Learning [4L] :Types of learning, general learning model, Learning by induction: generalization, specialization; example of inductive learner. WEB TECHNOLOGY (CS 7112) Static Web Pages [6L] Web Pages - types and issues, tiers; comparisons of Microsoft and java technologies, WWW-Basic concepts, web client and web server, http protocol (frame format), universal resource locator (url), HTML- different tags, sections, image & pictures, listings, tables, frame, frameset, form. Dynamic Web Pages [2L] The need of dynamic web pages; an overview of DHTML, cascading style sheet (css), comparative studies of different technologies of dynamic page creation. Active Web Pages [2L] Need of active web pages; java applet life cycle. Java Script [3L] Data types, variables, operators, conditional statements, array object, date object, string object. Java Servlet [4L] Servlet environment and role, HTML support, Servlet API, The servlet life cycle, Cookies and Sessions. JSP [15L] JSP architecture, JSP servers, JSP tags, understanding the layout in JSP, Declaring variables, methods in JSP, inserting java expression in JSP, processing request from user and generating dynamic response for the user, inserting applets and java beans into JSP, using include and forward action, comparing JSP and CGI program, comparing JSP and ASP program; Creating ODBC data source name, introduction to JDBC, prepared statement and callable statement. J2EE[7L] An overview of J2EE web services, basics of Enterprise Java Beans, EJB vs. Java Beans, basics of RMI, JNI. XML [6L] Extensible Markup Language (XML), basics of XML, elements and attributes, document type definition, XML parsers, sequential and tree approach. ELECTIVES I & II PARALLEL PROGRAMMING (CS 7114) Processes and processors. Shared memory. Fork. Join constructs. Basic parallel programming techniques- loop splitting, spin locks, contention barriers and row conditions. [ 12 L ] Variations in splitting, self and indirect scheduling. Data dependency-forward and backward block scheduling. Linear recurrence relations. Backward dependency. Performance tuning overhead with number of processes, effective use of cache. [ 12L ] Parallel programming examples: Average, mean squared deviation, curve fitting, numerical integration, travelling salesman problem, Gaussian elimination. Discrete event time simulation. [ 10 L ] Parallel Programming constructs in HPF, FORTRAN 95. Parallel programming under Unix. DATA WAREHOUSING AND DATA MINING (CS 7115) Introduction [2L] : Data warehousing – definitions and characteristics, Multi-dimensional data model, Warehouse schema. Data Marts [4L] : Data marts, types of data marts, loading a data mart, metadata, data model, maintenance, nature of data, software components; external data, reference data, performance issues, monitoring requirements and security in a data mart. Online Analytical Processing [4L] : OLTP and OLAP systems, Data Modeling, LAP tools, State of the market, Arbor Essbase web, Microstrategy DSS web, Brio Technology, star schema for multi dimensional view, snowflake schema; OLAP tools. Developing a Data Warehousing [4L] : Building of a Data Warehousing, Architectural strategies & organizational issues, design considerations, data content, distribution of data, Tools for Data Warehousing Data Mining [4L] : Definitions; KDD(Knowledge Discovery database) versus Data Mining; DBMS versus Data Mining, Data Mining Techniques; Issues and challenges; Applications of Data Warehousing & Data mining in Government. Association Rules [4L] : A priori algorithm, Partition algorithm, Dynamic inset counting algorithm, FP – tree growth algorithm; Generalized association rule. Clustering Techniques [4L] : Clustering paradigm, Partition algorithms, CLARA, CLARANS; Hierarchical clustering, DBSCAN, BIRCH, CURE; Categorical clustering, STIRR, ROCK, CACTUS. Decision Trees [4L] : Tree construction principle, Best split, Splitting indices, Splitting criteria, Decision tree construction with presorting. Web Mining [4L] : Web content Mining, Web structure Mining, Web usage Mining, Text Mining. Temporal and Spatial Data Mining [5L] : Basic concepts of temporal data Mining, The GSP algorithm, SPADE, SPIRIT, WUM. ROBOTICS (EC 7114) Robot Anatomy Arm Geometry-Direct & Inverse Kinematics Problem.Arm Dynamics,D Alembert Equations of Motion, Synthesis of elements with movalulity constraints,manipulations-trajectory planning,joint interpolated trajectories. [15L] Control of Robot Manipulation-computed torque technique sequencing & adaptive control, resolved motion control Moluie Robots. [6L] Robot sensing-Range & Proximity & Higher-Level vision, illumination techniques,Imaging Geometry, Segmentation Recognition & Interpretation. [8L] Robot Programming Language Characteristics of Robot Level & Task Level languages.Robot intelligence-State Space search, Robot learning,Robot Task Planning,Knowledge Engineering. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING (EC 7115) 4 Digital image fundamentals: - Image digitization 1L Sampling & quantisation 1L Image resolution 1L Colour perception & processing 1L Image processing: - Pixel based transformation 1L Geometric transformation 1L Local processing: - Edge detection, subpixel location estimation Restoration: - Degradation, inverse fitting, Wiener filtering 1L Binary image processing: - Thresholding, run length encoding 2L Distance transforms, Medial axis transforms 2L Morphological operations 1L Region segmentation & Representation: - Split & merge algorithm 1L Region growing 1L Image filtering: - Histogram modification 1L Linear & Gaussian filters 2L Contours: - Digital curves 3L Poly line splitting 2L Hop along algorithm 2L Conic & Splines Hough transform 2L Fourier description 2L Textures: - Statistical syntactic & model based methods 2L Image transforms: - Fourier, Hadamard, Discrete Cosine 2L Wavelets & other orthogonal transforms 2L Compression of image: - Predictive compression methods, vector quantisation, hierarchical & progressive methods, JPEG, MPEG 3L Case studies 3L MULTIMEDIA TECHNOLOGY(IT 7107) Introduction to Multimedia: Concepts, uses of multimedia, hypertext and hypermedia.; Image, video and audio standards. [ 8 L ] Audio: digital audio, MIDI, processing sound, sampling, compression. [6 L ] Video: MPEG compression standards, compression through spatial and temporal redundancy, inter-frame and intra-frame compression . [ 8 L ] Animation: types, techniques, key frame animation, utility, morphing. [ 6 L ] Virtual Reality concepts. [ 2 L ] Windows concepts and terminology, key elements Creating the look, communication via messages, windows resources and functions, adding multimedia and sound resources. Writing windows applications, taking control of windows, adding menus, dialog boxes, DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (EC 7110) Introduction, Overview of digital signal processing. 2 L Discrete – Time linear system, Sequences, arbitrary sequences, linear time invariant system, causality, stability. Difference equation, relation between continuous and discrete system. Classifications of sequence, recursive and non-recursive system. 8 L Mathematical operations on sequences: Convolution, graphical and analytical techniques, overlap and add methods, matrix method, some examples and solutions of LTI systems, MATLAB examples (Tutorial) 4 L Z-transform: Definition, relation between Z transform and Fourier transform of a sequence, properties of Z transform, mapping between S-plane and Z-plane. Unit circle, convergence and ROC, Inverse z-transform, solution of difference equation using the one sided Z-transform MATLAB examples (Tutorial). 6 L Discrete Fourier transform: Definition, inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) Twiddle factor, linear transformation, basic properties, circular convolution, multiplication of DFT, linear filtering using DFT, filtering of long data sequences, overlap add and save method. Computation of DFT, Fast Fourier transform (FFT), FFT algorithm, Radix 2 algorithm. Decimation-in-time and decimation-in- frequency algorithm, signal flow graph, butterflies, Chirp z-transform algorithm, MATLAB examples (Tutorial). 1 0 L Digital filter realization: Principle of digital filter realization, structures of All-zero filters. Design of FIR (Finite impulse response) filters, linear phase, windows-rectangular, Berlitt, Hanning, Hamming and Blackman. Design of infinite impulse response filters (IIR) from analog filters. Bilinear transformation, Butterworth, Chebyshev, Elliptic filters. Optimisation method of IIR filters. Some example of practical filter design. Computer aided filter design, MATLAB examples (Tutorial). 1 0 L BIOMEDICAL ELECTRONICS (EC 7116) Origin of bio-potential: Electric activity of excitable cells, resting potential, action potential, Nerst equation, propagation of action potential. Surface map of bio-potential- concept. 3L Biomedical electrodes: Electrode theory. Working principle & application of different bio-potential electrodes & biochemical transducerso Microelectrodes, surface electrodes, needle electrodes o Reference electrode, pH electrode, blood gas electrode 4L o Ion electrode. Cardiovascular measurements: Brief description of cardiovascular system. Electrocardiographyo Sources of cardiac bio-potentials, o Methodology & principle of measurement o Electrocardiograms & their inferences Vector cardiography- concept Principles of direct & indirect measurement of blood pressure Principles of measurement of blood flow/cardiac rate PH & blood gas analyzer 8L Electroencephalography (EEG): Sources of action potentials Methodology & principle of measurement Electroencephalograms & their inferences 4L Electromyography: Sources of action potentials Methodology & principle of measurement Electromyograms & their inferences 4L Respiratory system measurement: Respiratory mechanism, parameters of respiratory system Principle of measurement of various parameters, impedance pneumograph, Spiro meter. 4L Medical imaging systems: Working principles of medical X-ray, CT scan, CAT scan, Ultrasound scanning, MRI 4L Therapeutic & prosthetic devices: Pacemakers, Defibrillators, ventilators, respirators, heamodialysis machine 4L Medical application of LASER including safety aspects 2L Fiber optic application in imaging internal organs 1L Effect of mm wave and microwave on human body 1L Electrical safety: Physiological effect of electricity, micro shock & macro shock hazards, electrical safety standards for human body, basic approaches to shock protection. 1L OPERATIONS RESEARCH AND OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES (EC 7117) Introduction [2L] Introduction to OR modeling approach and various real life situations Linear programming problems [2L] Basic LPP and applications, Various components of LP problem formulation Solving Linear Programming problem [17L] Solving LPP using simultaneous equations and Graphical Method (2L) Simplex Method and extensions. (7L) Sensitivity analysis , Duality theory (2L) Revised Simplex, Transportation and assignment problems. (6L) Network Analysis [7L] Shortest paths, Maximal flow including PERT-CPM Integer programming [2L] Basic concepts, formulation, solution and applications Dynamic programming [4L] Modeling, Optimization, Replacement Game theory [4L] Introduction, Decisions under risk, Decisions under uncertainty Queuing Theory [7L] Introduction, basic definitions and notations, axiomatic derivation of the arrival & departure distributions for Poission Queue, Poission Queuing Model, M/M/1 queues in series, application GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM (CS 7116) Introduction and Overview of Geographic Information Systems [3L Definition of a GIS, features and functions; why GIS is important; how GIS is applied; GIS as an Information System; GIS and cartography; contributing and allied disciplines; GIS data feeds; historical development of GIS. GIS and Maps, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems [4L Maps and their characteristics (selection, abstraction, scale, etc.); automated cartography versus GIS; map projections; coordinate systems; precision and error. Data Sources, Data Input , Data Quality and Database Concepts [3L Major data feeds to GIS and their characteristics: maps, GPS, images, databases, commercial data; locating and evaluating data; data formats; data quality; metadata. Database concepts and components; flat files; relational database systems; data modeling; views of the database; normalization; databases and GIS. Spatial Analysis [3L Questions a GIS can answer; GIS analytical functions; vector analysis including topological overlay; raster analysis; statistics; integrated spatial analysis. Making Maps [6L Parts of a map; map functions in GIS; map design and map elements; choosing a map type; producing a map formats, plotters and media; online and CD-ROM distribution; interactive maps and the Web. Implementing a GIS [4L Planning a GIS; requirements; pilot projects; case studies; data management; personnel and skill sets; costs and benefits; selecting a GIS package; professional GIS packages; desktop GIS; embedded GIS; public domain and low-cost packages. Technology & Instruments involved in GIS & Remote Sensing [8L] GIS applications; GIS application areas and user segments; creating custom GIS software applications; user interfaces; case studies. Future data; future hardware; future software; Object-oriented concepts and GIS; future issues – data ownership, privacy, education; GIS career options and how to pursue them. Remote Sensing [8L Remote sensing of environment, E.M. Principle, Thermal infrared remote sensing, Remote sensing of Vegetation, Remote sensing of water, urban landscape SEMESTER-VIII E-COMMERCE & SECURITY(CS 8117) Introduction to E-Commerce [6L]: Definition, Scope of E-Commerce, Hardware requirements, E-Commerce and Trade Cycle, Electronic Markets, Electronic Data Interchange and Internet Commerce. Business to Business E-Commerce [7L]: Electronic Markets, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): Technology, Standards (UN/EDIFACT), Communications, Implementations, Agreements, Security, EDI and Business, Inter-Organizational E-commerce. Legal issues [5L]: Risks: Paper Document vs. Electronic document, Authentication of Electronic document, Laws, Legal issues for Internet Commerce: Trademarks and Domain names, Copyright, Jurisdiction issues, Service provider liability, Enforceable online contract. Security Issues [6L]: Security Solutions: Symmetric and Asymmetric Cryptosystems, RSA, DES, and Digital Signature, Protocols for secure messaging, Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Protocol, Electronic cash over internet, Internet Security. Business to Consumer E-Commerce [8L]: Consumer trade transaction, Internet, Page on the Web, Elements of E-Commerce with VB, ASP, SQL. E-business [7L]: Internet bookshops, Software supplies and support, Electronic Newspapers, Internet Banking, Virtual Auctions, Online Share Dealing, Gambling on the net, E-Diversity, Case studies through internet. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT & ACCOUNTING (CS 8118) Introduction [3L] Financial Management, Financial Planning and Capitalization- definitions, objectives, changing roles and functions, Financial Decision. Capital Budgeting [7L] Nature of Investment decision, Importance of Capital Budgeting, The Capital. Budgeting Process - Investment Criterion, Pay-back period, Accounting, ROR (Rate of Return) Method, Discounting Cash flow method, Net – present value method, IRR (Internal Rate of Return) method, The benefit-Cost Ratio method. Management of Working Capital [7L] Various concepts, Elements, Classification, Financing and importance of working capital, Investment analysis, Cash flow determination, cost of capital, capital budgeting methods. Budgeting Control Technique [5L] Concepts of Budget, budgeting and budgetary control, Objectives, Functions, Uses, Advantages, Limitations; Master Budget and Report. Cost – Volume – Profit Analysis [8L] Classification of costs, Allocation, apportionment and absorption, Cost centers, different costing systems, Cost analysis for managerial decisions, Meaning of Linear CVP analysis, Objectives, Assumptions, Break – Even analysis, determining the Break-Even point profit, Volume graph profit, Volume ratios margin of Safety. Introduction to Accounting [8L] Basic accounting concepts, important definitions, uses, limitations, advantages; types of Accounting, Financial statements, introduction to Journal Accounting; different types of Vouchers, double entry bookkeeping, different types of transactions related to Financial Accounting. Financial Control [7L] Posting of Ledgers and preparation of Trial Balance; preparation of Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Accounts; Controlling other departments by Financial Accounting (A practical Approach). ELECTIVES III, IV & V NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING (CS 8119) Introduction to NLP [2L]: Definition, issues and strategies, application domain, tools for NLP, Linguistic organisation of NLP, NLP vs PLP. Word Classes [13L]: Review of Regular Expressions, CFG and different parsing techniques 1L Morphology: Inflectional, derivational, parsing and parsing with FST, Combinational Rules 3L Phonology: Speech sounds, phonetic transcription, phoneme and phonological rules, optimality theory, machine learning of phonological rules, phonological aspects of prosody and speech synthesis. 4L Pronunciation, Spelling and N-grams: Spelling errors, detection and elimination using probabilistic models, pronunciation variation (lexical, allophonic, dialect), decision tree model, counting words in Corpora, simple N-grams, smoothing (Add One, Written-Bell, Good-Turing), N-grams for spelling and pronunciation. 5L Syntax [7L]: POS Tagging: Tagsets, concept of HMM tagger, rule based and stochastic POST, algorithm for HMM tagging, transformation based tagging 4L Sentence level construction & unification: Noun phrase, co-ordination, sub-categorization, concept of feature structure and unification. 3L Semantics [9L]: Representing Meaning: Unambiguous representation, canonical form, expressiveness, meaning structure of language, basics of FOPC 2L Semantic Analysis: Syntax driven, attachment & integration, robustness 2L Lexical Semantics: Lexemes (homonymy, polysemy, synonymy, hyponymy), WordNet, internal structure of words, metaphor and metonymy and their computational approaches 3L Word Sense Disambiguation: Selectional restriction based, machine learning based and dictionary based approaches. 2L Pragmatics[8L]: Discourse: Reference resolution and phenomena, syntactic and semantic constraints on Coreference, pronoun resolution algorithm, text coherence, discourse structure 4L Dialogues: Turns and utterances, grounding, dialogue acts and structures 1L Natural Language Generation: Introduction to language generation, architecture, dicourse planning (text schemata, rhetorical relations). MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM(IT 7106) 1. Introduction(2L) Definition of management, its definition, purpose, elements of science, patterns of management analysis. Functions of managers. 2. People & organization. (6L) People: psychological factors, worker’s skill & abilities. Organization:Organizational characteristics, Organizational behavior, corporate culture, power inter-group conflict, intra-group dynamics, the MIS function in organization, MIS personal, computer operation personal, MIS management. 3. System & models. (6L) System: components of a system, environment, open Vs Closed systems. Models: modeling systems general vs specific models, levels of models, types of models. Models of organizational systems. A general model of organization and its internal environment. Strategic planning models. 4. Management & decision making (5L) Management: labels of management, managerial role, planning & control, Managerial styles, Managerial decision making: characteristics of types of decision 5. Decision making process. (3L) Intelligence, design, soln evaluation & choice. 6. Evaluating decision making.(2L) Effectiveness vs efficiency 7. Transaction processing & management reporting systems.(5L) A management information systems frame work: ----- Transaction processing framework ----- Management reporting system ----- Decision support system. ----- Knowledge based systems ----- Office systems 8. Transaction processing.(2L) nature function role of IT in transaction processing processing cycles Transaction processing subsystem. 9. Management reporting system. (2L) Evaluation of management reporting system, types of reports, structuring report content. 10. Decision support system (DSS). (3L) Component of DSS DSS development DSS products DSS development tools User interfaces Executive information system (EIS) Executive roles & decision making. Executive decision making environment 11. MIS in the functional areas of business. (3L) Financial information system, Marketing MIS Manufacturing MIS 12. Enterprise resource planning (3L) Materials Requirement planning (MRP) Closed loop MRP Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP – II) ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING Functional architecture of ERP Benefits of ERP Business Process Reengineering and ERP ERP implementation 13. Supply chain management (1L) Introduction Definition of SCM Features of SCM SCM Stages 14. Cases in MIS (2L) Case study method Analytical Case Issue Case Written Case Analysis Illustrations ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING (EC 8124) 1. Electronic Commerce : Overview, Definitions, Advantages & Disadvantages of E – Commerce, Threats of E – Commerce, Managerial Prospective, Rules & Regulations For Controlling E – Commerce, Cyber Laws. [ 3 L ] 2. Technologies : Relationship Between E – Commerce & Networking, Different Types of Networking For E – Commerce, Internet, Intranet & Extranet, EDI Systems Wireless Application Protocol : Definition, Hand Held Devices, Mobility & Commerce, Mobile Computing, Wireless Web, Web Security, Infrastructure Requirement For E – Commerce . [ 5L ] 3. Business Models of e – commerce : Model Based On Transaction Type, Model Based On Transaction Party - B2B, B2C, C2B, C2C, E – Governance. [2 L ] 4. E – strategy : Overview, Strategic Methods for developing E – commerce. [2 L ] 5. Four C’s : ( Convergence, Collaborative Computing, Content Management & Call Center ). Convergence : Technological Advances in Convergence – Types, Convergence and its implications, Convergence & Electronic Commerce. Collaborative Computing : Collaborative product development, contract as per CAD, Simultaneous Collaboration, Security. Content Management : Definition of content, Authoring Tools & Content Management, Content – partnership, repositories, convergence, providers, Web Traffic & Traffic Management ; Content Marketing. Call Center : Definition, Need, Tasks Handled, Mode of Operation, Equipment , Strength & Weaknesses of Call Center, Customer Premises Equipment (CPE). [ 6 L ] 6. Supply Chain Management : E – logistics, Supply Chain Portal, Supply Chain Planning Tools (SCP Tools), Supply Chain Execution (SCE), SCE - Framework, Internet’s effect on Supply Chain Power. [ 3 L ] 7. E – Payment Mechanism : Payment through card system, E – Cheque, E – Cash, E – Payment Threats & Protections. 8. E – Marketing :. Home –shopping, E-Marketing, Tele-marketing [[[[[[[[ 9. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) : Meaning, Benefits, Concepts, Application, EDI Model, Protocols (UN EDI FACT / GTDI, ANSI X – 12), Data Encryption (DES / RSA). [2 L ] 10. Risk of E – Commerce : Overview, Security for E – Commerce, Security Standards, Firewall, Cryptography, Key Management, Password Systems, Digital certificates, Digital signatures. [4 L ] 11. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Features, capabilities and Overview of Commercial Software, re-engineering work processes for IT applications, Business Process Redesign, Knowledge engineering and data warehouse . Business Modules: Finance, Manufacturing (Production), Human Resources, Plant Maintenance, Materials Management, QualityManagement, Sales&Distribution ERPPackage, ERP Market: ERP Market Place, SAP AG, PeopleSoft, BAAN, JD Edwards, Oracle Corporation ERP-Present and Future: Enterprise Application Integration (EAI), ERP and E-Commerce, ERP and Internet, Future Directions in ERP WIRELESS COMMUNICATION (EC 7112) Introduction to Wireless Communication Systems – evolution of mobile radio communications, mobile radio systems around the world, radio communication systems – paging systems, cordless telephone systems, cellular telephone systems; comparison of common wireless communications, trends in cellular radio and personal communication, second generation (2G) cellular networks, third generation (3G) wireless networks, introduction to radio wave propagation, free space propagation model 10L Basics of mobile communication – Limitations of conventional mobile system, mobile cellular communication – introduction, concept of frequency reuse, cluster size, cellular system architecture – mobile station, base station, MSC, channel assignment strategies, call handover strategies, interference and system capacity, improving capacity in cellular systems – cell splitting, sectoring, repeaters, microcell zone concept. 12L Global system for mobile communication – GSM services and features, system architecture, GSM radio subsystem, GSM channel types, location updating and call setup, introduction to CDMA digital cellular standard, comparison between GSM and CDMA. 10L Wireless networking – wireless local area network standards, technology – RF and IR wireless LAN, diffuse, quasi-diffuse and point-to-point IR wireless LAN, advantages and applications of Wireless LAN, introduction to WI-FI, Bluetooth, 3G and 4G wireless systems 8L [[ FIBER NETWORKS (EC 8125) : 4 Introduction: - Basics of Optical bench, Fibre–end preparation of fibre ends, launching mechanism of light into fibre end, coupling of light into detector. 4L Measuring Instruments: - Lock-in-Amplifier, Monochromator, Infrared viewer, Optical Spectrum Analyser, OTDR. 2L Multi-mode fibre: – Parameters for characterisation, Steady-State Power distribution, mode stripper. 2L Measurements of attenuation: - Loss Mechanisms in Fibre, Calorimetric Method, Absorption & Scattering losses, Differential mode attenuation, Cut-Back method, OTDR techniques; Numerical Aperture- trigonometric & Scanning methods. 8L Refractive Index Profile: - Reflection method, Near Field Scanning, Refracted Near Field methods, Interferometric Slab technique 6L Dispersion Measurements: - Time-Domain Method & Frequency Domain Method 5L Geometrical Measurements: - diameter, deformation, eccentricity, ellipticity. 2L Single–mode Fibre: – Mode Cut-Off wavelength, Mode-field Diameter, Equivalent Step-Index (ESI) Profile, Dispersion, Birefringence Measurement 7L Mechanical Strength of Optical Fibre 2L International Standards for Measurements: World Bodies, RTM, ATM, Recommendations 2L COMPUTER VISION (CS 7118) Discrete geometry & quantization 2L Length estimations 1L Automated visual inspection 2L Object recognition & matching 3L Depth perception problems 2L Stereo geometry & correspondence 4L Motion analysis 3L Optical flow 2L Application of computer vision 4L Remote sensing 4L Bio-medical imaging 4L Document processing 4L Target tracking 4L INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (IT 7108) An Overview on Internet [4L] The need for an Internet, The TCP/IP Internet, Internet services, Internet protocols and standardization, Review of Network technologies. Internetworking Concepts [6L] Architectural model introduction, Application level interconnection, Network level interconnection, Properties of the Internet, Internet Architecture, Interconnection through IP Gateways or routers, Internet and Intranet. Internet Address [5L] Introduction, Universal identifiers, Three primary classes of IP addresses, Classless IP address, Network and Broadcast addresses, Mapping internet addresses to physical addresses (ARP), ARP protocol format, Transport Gateways and subnet addressing, Multicast addressing. Internet Protocol [6L] Internet Architecture and Philosophy, The concept of unreliable delivery, Connectionless delivery system, The Internet Datagram, Routing direct and indirect delivery, Table driven IP routing, Protocol layering, Reliable stream transport, TCP performance, Bootstrap protocol (BOOTP). Routing [7L] The origin of Gateway routing tables, Original Internet Architecture and Cores, Core Gateways, Automatic route propagation, Vector distance (Bellman-Ford), routing, Gateway to Gateway Protocol (GGP), Autonomous system concept, Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), Interior Gateway Protocol (RIP, OSPF, HELLO), Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Combining RIP, HELLO, and EGP, Routing with partial information. Enterprise Networking [7L] Corporate networking, Broadband at the Metropolitan area level, High speed dedicated WAN services and switched WAN services, ISDN, BISDN and ATM services, Frame relay technology and services, Virtual private network concepts PPTP protocol. Internet Servers [4L] DNS, DHCP Servers, FTP, TELNET, E-Mail Firewall & Networking [6L] Introduction, Implementation of Firewall, Activities of Firewall, Configuration of firewall, Firewalls & SSL, SSL implementation, Bit implementation of SSL, Use of SSL. LINUX PROGRAMMING & SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (CS 8120) Introduction to System Administration [ 4 L ] Essential Administrative Tools. [ 4 L ] Starting and shutdown [ 4L ] User Accounts [ 4 L ] Security [ 4 L] TCP / IP Network Management [ 4L] Getting started in LINUX. [ 2 L ] Linux Data Management [ 4 L ] POSIX Threads [4 L] Pipes, Semaphores, Message Queues, Shared Memory, Sockets [ 2 L ] Tool Command Language [ 2 L ] PERL & CGI. REAL TIME & EMBEDDED SYSTEM (EC 7113) Introduction-defining Real time systems,Embedded Real Time Systems,Special Characteristics of real time systems,a brief evolutionary history. Hardware Architectures of Real Time systems. [12L] Software architectures(concepts of interrupt driven activation,need for real time monitor,pseudo parallelism),meeting of dead lines & real time constraints.[5L] Overview of WARD & MELLOR Methodology: Ward & Mellor Life Cycle,the essential model step,the implementation model,real time extensions of DFD[10L] Real time languages: overview of ADA/Java Extension [4L] Real time Operating Systems . [4L] System Development Methodologies. BIO INFORMATICS (IT 8110) Introduction to Genomic data and Data Organization: Sequence Data Banks – Introduction to sequence date banks – protein sequence data bank. NBFR-PIR, SWISSPROT, Signal peptide data bank, Nucleic acid sequence data bank – GenBank, EMBL nucleotide sequence data bank, AIDS virus sequence data bank. RRNA data bank, structural data banks – protein Data Bank (PDB), The Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) : Genome data bank – Metabolic pathway data : Microbial and Cellular Data Banks. Introduction to MSDN (Microbial Strain Data Network): Numerical Coding Systems of Microbes, Hibridoma Data Bank Structure, Virus Information System Cell line information system; other important Data banks in the area of Biotechnology/life sciences/biodiversity. Sequence analysis: Analysis Tools for Sequence Data Banks; Pair wise alignment - NEEDLEMAN and Wunsch algorithm, Smith Waterman, BLAST, FASTA algorithms to analyze sequence data: Sequence patterns motifs and profiles. Secondary Structure predictions; prediction algorithms; Chao-Fasman algorithm, Hidden- Markov model, Neural Networking. Tertiary Structure predictions; prediction algorithsms; Chao-Fasman algorithm, Hidden- Markov model, Neural Neworking. Applications in Biotechnology: Protein classifications, Fold libraries, Protein structure prediction: Fold recognition (threading), Protein structure predictions : Comparative modeling (Homology), Advanced topics: Protein folding, Protein-ligand interactions, Molecular Modeling & Dynamics, Drug Designing. INFORMATION & CODING THEORY(CS 8121) Source Coding [7L] Uncertainty and information, average mutual information and entropy, information measures for continuous random variables, source coding theorem, Huffman codes. Channel Capacity And Coding [7L] Channel models, channel capacity, channel coding, information capacity theorem, The Shannon limit. Linear And Block Codes For Error Correction [8L] Matrix description of linear block codes, equivalent codes, parity check matrix, decoding of a linear block code, perfect codes, Hamming codes. Cyclic Codes [7L] Polynomials, division algorithm for polynomials, a method for generating cyclic codes, matrix description of cyclic codes, Golay codes. BCH Codes [8L] Primitive elements, minimal polynomials, generator polynomials in terms of minimal polynomials, examples of BCH codes. Convolutional Codes [8L] Tree codes, trellis codes, polynomial description of convolutional codes, distance notions for convolutional codes, the generating function, matrix representation of convolutional codes, decoding of convolutional codes, distance and performance bounds for convolutional codes, examples of convolutional codes, Turbo codes, Turbo decoding. VALUES & ETHICS OF PROFESSION (IT 6105) Science, Technology and Engineering as knowledge and as Social and Professional Activities Effects of Technological Growth: Rapid Technological growth and depletion of resources, Reports of the Club of Rome. Limits of growth: sustainable development Energy Crisis: Renewable Energy Resources Environmental degradation and pollution. Eco-friendly Technologies. Environmental Regulations, Environmental Ethics Appropriate Technology Movement of Schumacher; later developments Technology and developing notions. Problems of Technology transfer, Technology assessment impact analysis. Human Operator in Engineering projects and industries. Problems of man, machine, interaction, Impact of assembly line and automation. Human centered Technology. Ethics of Profession: Engineering profession: Ethical issues in Engineering practice, Conflicts between business demands and professional ideals. Social and ethical responsibilities of Technologists. Codes of professional ethics. Whistle blowing and beyond, Case studies. Profession and Human Values: Values Crisis in contemporary society Nature of values: Value Spectrum of a good life Psychological values: Integrated personality; mental health Societal values: The modern search for a good society, justice, democracy, secularism, rule of law, values in Indian Constitution. Aesthetic values: Perception and enjoyment of beauty, simplicity, clarity Moral and ethical values: Nature of moral judgements; canons of ethics; ethics of virtue; ethics of duty; ethics of responsibility. |
|
#12
15th November 2012, 11:32 PM
|
|||
|
|||
|
Syllabus for B.Sc(Computer Science) ::
-->> Language (Tamil/Telugu/Hindi) -->> English Language -->> Mathematics Paper -->> Digital Logic fundamentals -->> Operating System -->> Programming in C -->> C Lab -->> C++ and Data Structure -->> Data Structure using c++ Lab -->> MicroProcessor & It is applications -->> Software engineering -->> RDMBS with Oracle -->> Programming in C# -->> C# Lab thaxsxsxs |
Related Topics: |
||
| Thread | Replies | Last Post |
| Which course is a better choice for me between M.Tech in Computer Science and Ph.D in Computer Science having completed MCA and M.Sc in Computer Science? | 5 | 27th October 2013 02:04 PM |
| What is M.Tech syllabus for computer science and computer network category from VTU university | 2 | 15th April 2013 12:41 PM |
| How may I get syllabus of entrance exam for B.Tech(computer science) after completing polytechnic(computer science and engineering)? | 3 | 7th June 2012 04:44 PM |
|
|